Sustainable Water Infrastructure Contacts
Pacific Southwest, Region 9
Serving: Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, Pacific Islands, Tribal Nations
Water & Energy Efficiency in Water and Wastewater Facilities
| Sustainable Water Infrastructure Quick Finder | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FundingGreen Jobs in the Water SectorLow Impact Development | Waste To Biogas Mapping ToolWater Conservation/EfficiencyWater-Energy Connection | Water Loss ControlWhy Sustainability? | ||
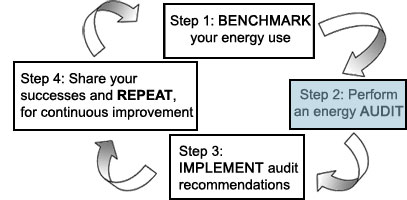
Step 2: Perform an Energy Audit
On this page:
- What Are Energy Audits?
'Do It Yourself' Energy Audit Guidance - Who Performs Energy Audits?
DOE's Industrial Assessment Centers - How Much Do Energy Audits Cost?
Model Energy Audit Request for Proposal - Case Studies and Example Audits
What Are Energy Audits?
Performing an energy audit is a crucial step to assessing and improving energy efficiency. There are many types of energy audits that can be performed at water and wastewater treatment facilities, ranging from general 'walk-through audits' to more comprehensive 'process audits.'
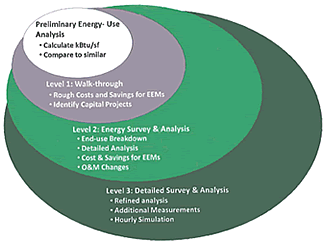
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) refers to benchmarking as a preliminary energy use analysis; this process involves collecting facility energy data, reviewing energy bills, and comparing the facility's energy consumption with similarly-sized facilities using similar processes. EPA’s Energy Star's Portfolio Manager is a free, on-line benchmarking tool. EPA recommends all facilities use Portfolio Manager or another benchmarking tool prior to completing a walk-through or detailed process audit.
EPA's Energy Use Assessment Tool
This Excel-based tool can be used by small- to medium-sized systems to conduct a utility bill and equipment analysis to assess individual baseline energy use and costs.
- Energy Use Tool Assesment Overview (PDF)
(60 pp, 2.9MB) - Energy Use Assessment Tool (XLS)
(4.1MB - Right Click/Save As) - Energy Use Assessment Tool with example Data (XLS) (4.25MB - Right Click/Save As)
- Energy Use Assessment Tool User's Guide (PDF)
(67 pp, 1.5MB)
'DIY' Guidance from the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority
DOE's Industrial Assessment Centers
The Department of Energy's (DOE) Industrial Assessment Centers (IACs) ![]() provide eligible industrial facilities (including drinking and wastewater treatment facilities) with no-cost detailed process audits. To be eligible for an audit, a facility's annual energy costs must exceed $100,000. There are two IACs within Region 9: The San Francisco State University IAC
provide eligible industrial facilities (including drinking and wastewater treatment facilities) with no-cost detailed process audits. To be eligible for an audit, a facility's annual energy costs must exceed $100,000. There are two IACs within Region 9: The San Francisco State University IAC ![]() and the San Diego State University IAC.
and the San Diego State University IAC. ![]()
Walk-through (also called ASHRAE Level 1) audits provide a “first cut” assessment of energy savings; they’re especially valuable to small utilities with simple production and distribution systems, and facilities that have never received an energy audit. While walk-through audits lack a detailed analysis of potential energy efficiency measures (and only sometimes include rough pay-back period estimates), they reliably include relatively simple and immediately affordable recommendations—such as changes in operation timing (based on utility rate schedules), and upgrades to lighting, heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC), and pumping equipment. For a small facility, a walk-through audit can be completed in 2-6 hours by someone familiar with the system. A number of entitles have provided ‘Do It Yourself’ guidance to assist facilities in conducting their own walk-through audits.
Detailed process audits (also called Level 2—or, if more refined—Level 3 ASHRAE audits) require a more in-depth conversation between the facility and professional auditors experienced in water and wastewater systems. Detailed process audits are the most cost-effective for mid-size and large facilities that lack in-house time to investigate energy efficiency opportunities, and that have not recently received an energy audit. Detailed process audits often involve equipment field tests, inventorying equipment energy performance data, creating energy profiles for equipment and systems, discussing potential O&M changes, and evaluating potential energy efficiency and renewable energy projects. Detailed process audits provide comprehensive information on the pay-back periods associated with the recommended measures.
Who Performs Energy Audits?
Audits can be performed by any combination electric and gas utility experts, water and wastewater facility staff, and outside energy specialists and contractors. The most important consideration is ensuring the auditor has water/wastewater treatment facility experience. Trade associations such as ASHRAE and the Association of Energy Engineers (AEE) offer a wide variety of certifications for energy auditors, but no group offers specialized credentials for the water and wastewater industry. Many electric and gas utilities offer audits through preselected contractors. In general, audits performed by an electric utility or contract auditor tend to focus on equipment upgrades with relatively short payback periods and maximizing rebates provided by the utility. Potential advantages of having audits performed by energy specialists with knowledge specific to the water and wastewater industry include: process suggestions that may have little or no capital costs, suggestions for operating more efficiently or improving water or effluent quality, suggestions that may help reduce chemical use, a comprehensive use of all energy in the plant (oil, gas, electric, and other sources) and analysis of the potential for energy production and water re-use.

How Much Do Energy Audits Cost?
The cost of audits varies by location and, of course, level of detail. Detailed process audits can take several days to complete, and can cost $5,000 to $25,000 or more depending on the size and complexity of the facility. In some areas, walk-through audits are free from electric and gas providers. In other areas, a fee is charged based on the level of audit required. Many electric and gas utilities will match up to 50% of an audit's cost.
The links below provide more information on who can perform an audit in your state and what incentives, rebates, and other resources are available to assist you.
Model Energy Audit Request for Proposal
If your facility would like to receive a detailed process audit, a Request for Proposals (RFPs) is a good place to begin the solicitation process.
The Maine Department of Environmental Protection's Model Energy Audit Request for Proposal (PDF) (6 pp, 86K) provides a guiding to template to assist facilities in developing an Energy Audit RFP.Arizona
- Salt River Project
 provides expert advice and discounts for specific energy upgrades.
provides expert advice and discounts for specific energy upgrades. - Arizona Public Service (APS)
 provides financial support for energy audits and other incentives for large and small customers.
provides financial support for energy audits and other incentives for large and small customers.
California
- California Energy Commission
 provides low interest loans for energy conservation feasibility studies.
provides low interest loans for energy conservation feasibility studies. - The California Public Utility Commission
 funds the California Wastewater Process Optimization Program (CalPOP) which provides free process audits, installs new equipment, and provides operator training.
funds the California Wastewater Process Optimization Program (CalPOP) which provides free process audits, installs new equipment, and provides operator training. - Pacific Gas & Electric Company
 provides two types of free energy audits: the on-site energy audit and the more comprehensive integrated energy audit.
provides two types of free energy audits: the on-site energy audit and the more comprehensive integrated energy audit. - San Diego Gas and Electric Company
 offers tools to monitor and track energy use.
offers tools to monitor and track energy use. - Southern California Edison (SCE)
 offers free energy assessments and additional financial incentives.
offers free energy assessments and additional financial incentives.
Hawaii
Within Hawaii, energy audits are offered by the four power utilities:
- Hawaiian Electric Company- HECO

- Maui Electric Company- MECO

- Hawaii Electric Light Company- HELCO

- Kauai Island Utility Cooperative- KIUC

HECO, MECO, and HELCO: Energy assessments are provided via self-audit materials such as the HECO/BOMA Hawaii guidebook which encourages companies to use the BOMA/EPA Energy Star® Energy Efficiency Program (BEEP®). ![]() Although HECO, MECO and HELCO do not pay for energy audits in their entirety, they will work with businesses to conduct "Energy or Feasibility Studies" and pay 50%, or up to $10,000.00 for each study. KIUC's Energy Wise Commercial Energy Efficiency Program
Although HECO, MECO and HELCO do not pay for energy audits in their entirety, they will work with businesses to conduct "Energy or Feasibility Studies" and pay 50%, or up to $10,000.00 for each study. KIUC's Energy Wise Commercial Energy Efficiency Program ![]() conducts free energy surveys to identify energy-saving measures and equipment replacement measures eligible for financial rebates and incentives.
conducts free energy surveys to identify energy-saving measures and equipment replacement measures eligible for financial rebates and incentives.
Nevada
In Nevada, energy audits are offered by the power utilities, Sierra Pacific and Nevada Power, via a contract program called Sure Bet. The Sure Bet Program offers both Prescriptive and Custom Incentives to Sierra Pacific Power and Nevada Power non-residential electricity customers. Funding is available for retrofit, new construction, walk-through inspections, and energy audits. Walk-through audits are free. A more comprehensive process audit to help fine-tune energy saving options is available for a nominal fee.
Case Studies and example audits
- Actual PG&E Customer Energy Efficiency Program (PDF) audit sample (5 pp, 290K, About PDF)
- Energy Audit Report for County of Kauai Waimea Wastewater Treatment Plant (PDF) (38 pp, 3.7MB)
- Energy Audit Report for County of Honolulu Kailua Wastewater Treatment Plant (PDF) (44 pp, 8.9MB)
- Energy Audit Report for County of Maui Kihei Wastewater Reclamation Facility (PDF) (40 pp, 9.2MB)
- Energy Audit Report for County of Hawaii Hilo Wastewater Treatment Plant (PDF) (46 pp, 9.6MB)