Global Mitigation of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gases: Solvents
Key Points
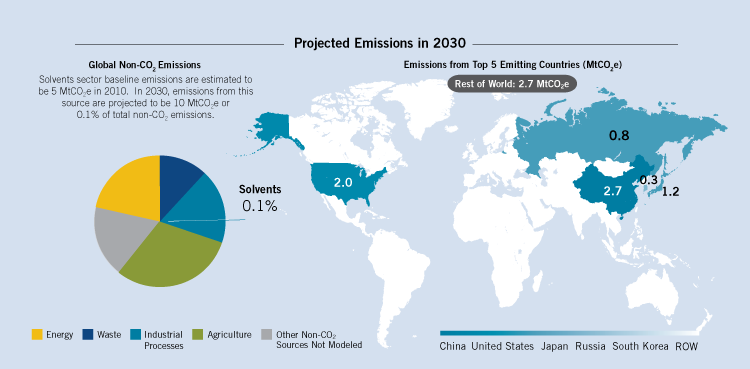
- By 2030, emissions from the solvents sector are expected to approximately double, reaching 10 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO2e).
- The maximum abatement potential in the solvents sector from the options analyzed is estimated to be 6 MtCO2e, or 59% of the projected baseline in 2030.
- 5 MtCO2e of emissions reductions in 2030 are cost-effective (i.e., $0/tCO2e or lower break-even prices).
Sector Description
Hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) solvents are primarily used in precision cleaning applications and electronic cleaning applications. Precision cleaning requires a high level of cleanliness to ensure the satisfactory performance of the product being cleaned, and electronics cleaning is defined as a process that removes contaminants, primarily solder flux residues, from electronics or circuit boards. It is assumed that eventually approximately 90% of the solvent consumed in a given year will be emitted, while 10% of solvent will be disposed of with the sludge that remains.
 View or download the full size image here.(121 K, PNG)
View or download the full size image here.(121 K, PNG)
Emissions Reduction Potential
Assuming full implementation of current technology, emissions in the solvents sector could be reduced by up to 6 MtCO2e in 2030. This accounts for 0.12% of the 4,615 MtCO2e in global reduction potential in 2030.
 View or download the full size image here.(94 K, PNG)
View or download the full size image here.(94 K, PNG)
Abatement Potential
The global abatement potential in 2020 and 2030 is 3.0 and 5.7 MtCO2e, respectively. In 2030, reduction of 4.8 MtCO2e , or 50%, of total projected emissions, is achievable at mitigation costs below $0/tCO2e. Additional abatement of approximately 1 MtCO2e is achievable at mitigation costs greater than $50/tCO2e.
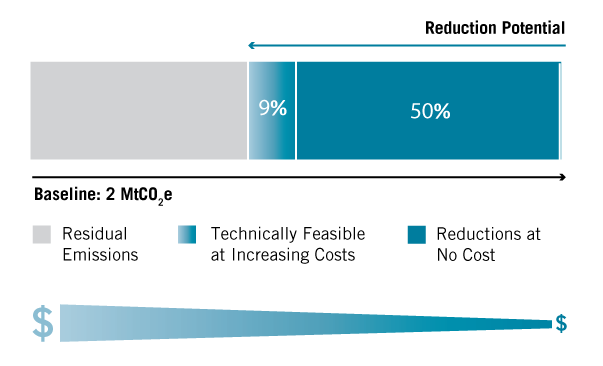 It would be cost-effective to reduce emissions by 50%, compared to the baseline, in 2030. An additional 9% reduction is available using technologies with increasingly higher costs.
It would be cost-effective to reduce emissions by 50%, compared to the baseline, in 2030. An additional 9% reduction is available using technologies with increasingly higher costs.
View or download the full size image here.(36 K, PNG)
Abatement Measures
Four abatement options were identified for the solvents sector: 1) replacement of HFCs with HFEs, 2) retrofitting of vapor degreaser equipment to reduce emissions, 3) transition to not-in-kind (NIK) aqueous cleaning, and 4) transition to NIK semi-aqueous cleaning. These technologies have reduction efficiencies of between 50% and 100%. Retrofitting equipment and controls is limited to facilities that have not already been retrofitted. Transition to NIK aqueous and NIK semi-aqueous applicability is limited to some electronic cleaning processes.
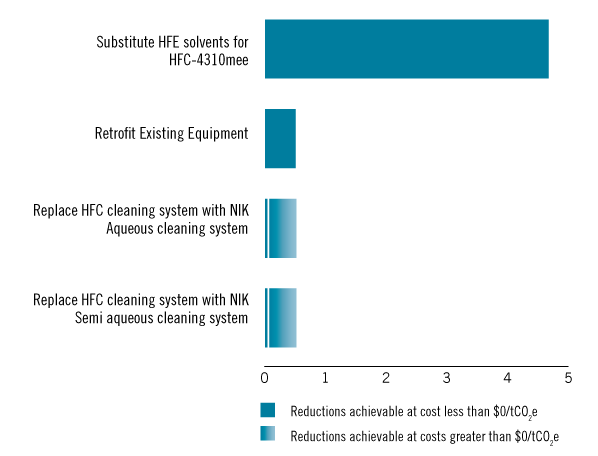 Emissions reductions by technology in 2030 at $0/tCO2e and at higher prices.
Emissions reductions by technology in 2030 at $0/tCO2e and at higher prices.
View or download the full size image here.(36 K, PNG)
