Global Mitigation of Non-CO2 Greenhouse Gases: HCFC-22 Production
Key Points
- Global abatement potential in the HCFC-22 production sector is 228 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent (MtCO2e) and 255 MtCO2e in 2020 and 2030, respectively, which equates to a 90% reduction from projected baseline emissions.
- Thermal oxidation is the only abatement option considered for the HCFC-22 production sector.
- The maximum abatement potential is achievable at costs below $1 per tCO2.
Sector Description
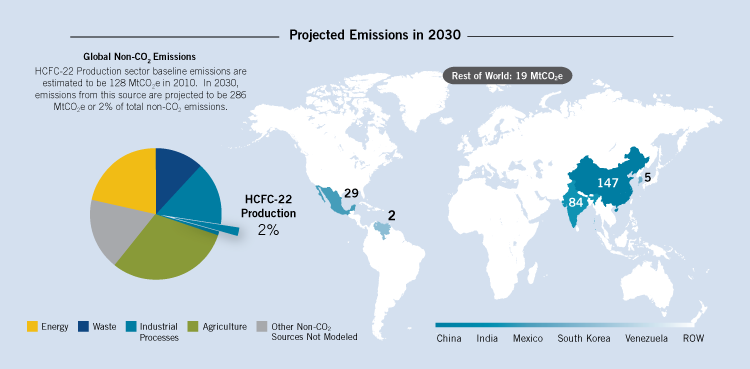
Chlorodifluoromethane (HCFC-22) is used in emissive applications (air conditioning and refrigeration) as well as in feedstock for synthetic polymer production. The production of HCFC-22 generates HFC-23 as a byproduct, which is separated as a vapor from the condensed HCFC-22; emissions occur through HFC-23 venting to the atmosphere. HFC-23 emissions were estimated at 128 MtCO2e and are projected to increase to 259 and 286 MtCO2e in 2020 and 2030, respectively. Because HCFC-22 depletes stratospheric ozone, its production is being phased out under the Montreal Protocol in areas apart from feedstock production.
 View or download the full-size image here.(120 K, PNG)
View or download the full-size image here.(120 K, PNG)
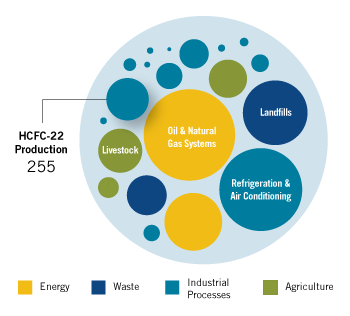
Emissions Reduction Potential
Assuming full implementation of current technology, emissions in the HCFC-22 production sector could be reduced by up to 255 MtCO2e in 2030. This accounts for 6% of the 4,615 MtCO2e in global reduction potential in 2030.
 View or download the full-size image here.(105 K, PNG)
View or download the full-size image here.(105 K, PNG)
Abatement Potential
Global abatement potential of HFC-23 in 2030 is 255 MtCO2e, approximately 89% of projected baseline emissions. The analysis assumes that facilities in most developed countries have already adopted abatement measures. As a result, abatement potential is limited to developing countries. Maximum abatement potential is achievable at a cost of between $0 and $1 per tCO2e.
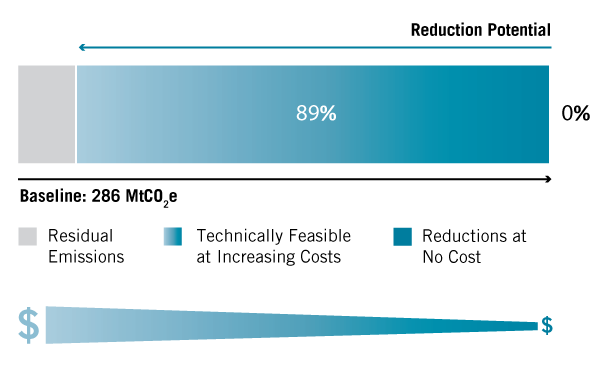 It would be cost-effective to reduce emissions by 0%, compared to the baseline, in 2030. An additional 89% reduction is available using technologies with increasingly higher costs.
It would be cost-effective to reduce emissions by 0%, compared to the baseline, in 2030. An additional 89% reduction is available using technologies with increasingly higher costs.
View or download the full-size image here.(37 K, PNG)
Abatement Measures
Thermal oxidation is the only abatement option considered in this analysis for the HCFC-22 production sector. Thermal oxidation is a demonstrated technology that oxidizes HFC-23 to carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrogen fluoride, and water for the destruction of halogenated organic compounds. This process is assumed to be compatible with all facilities.
 Emissions reductions by technology in 2030 at $0/tCO2e and at higher prices.
Emissions reductions by technology in 2030 at $0/tCO2e and at higher prices.
View or download the full-size image here.(32 K, PNG)
