Overview of the Oil and Natural Gas Industry
Oil and natural gas systems encompass wells, gas gathering and processing facilities, storage, and transmission and distribution pipelines. These components are all important aspects of the natural gas cycle—the process of getting natural gas out of the ground and to the end user.
- Natural Gas Systems - Industry Overview
- Primary Sources of Methane Emissions
- Estimates of Methane Emissions
Natural Gas Systems - Industry Overview
Natural gas systems encompass the following industry segments:
- Production: Taking raw natural gas from underground formations.
- Gathering and Processing: Stripping out impurities and other hydrocarbons and fluids to produce pipeline grade natural gas that meets specified tariffs (pipeline quality natural gas is 95-98 percent methane).
- Transmission: Delivery of natural gas from the wellhead and processing plant to city gate stations or industrial end users. Transmission occurs through a vast network of high pressure pipelines. Natural gas storage falls within this sector. Natural gas is typically stored in depleted underground reservoirs, aquifers, and salt caverns.
- Distribution: Delivery of natural gas from the major pipelines to the end users (e.g., residential, commercial and industrial).
In the oil industry, some underground crude contains natural gas that is entrained in the oil at high reservoir pressures. When oil is removed from the reservoir, associated natural gas is produced.
The diagram below displays the segments of the oil and natural gas industry and presents the top methane emission sources for each sector.
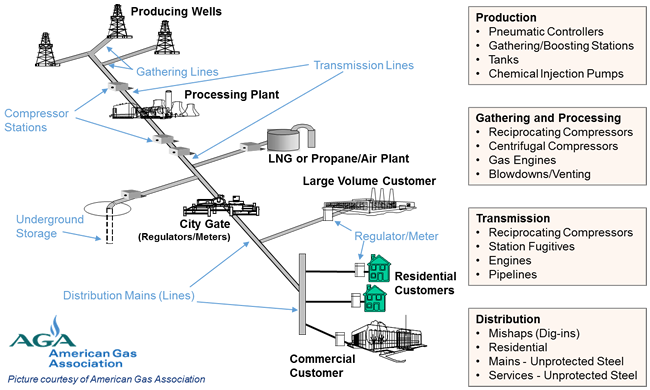 This diagram displays the segments of the oil and natural gas industry, including production, gathering and processing, transmission, and distribution, and presents the top methane emission sources for each sector.
This diagram displays the segments of the oil and natural gas industry, including production, gathering and processing, transmission, and distribution, and presents the top methane emission sources for each sector.
Primary Sources of Methane Emissions
Methane emissions occur in all sectors of the natural gas industry, from production, through processing and transmission, to distribution. They primarily result from normal operations, routine maintenance, fugitive leaks, and system upsets.
As gas moves through the system, emissions occur through intentional venting and unintentional leaks. Venting can occur through equipment design or operational practices, such as the continuous bleed of gas from pneumatic devices (that control gas flows, levels, temperatures, and pressures in the equipment), or venting from well completions during production. In addition to vented emissions, methane losses can occur from leaks (also referred to as fugitive emissions) in all parts of the infrastructure, from connections between pipes and vessels, to valves and equipment.
Methane emissions can also occur from the oil industry as result of:
- Field production operations: Venting of associated gas from oil wells and storage tanks
- Production-related equipment: Gas dehydrators, pig traps and pneumatic devices
Estimates of Methane Emissions by Sector in the United States
The EPA estimates methane emissions from the oil and natural gas industry in its annual Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks. Charts summarizing the 2014 methane emissions by sector in the oil and gas industry are presented below.
Overview
Aggregate methane emission estimates by the major oil and natural gas sectors in the United States are presented in the chart below.
| Segment | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Oil Production | 28 |
| Gas Production | 45 |
| Processing | 10 |
| Transmission and Storage | 13 |
| Distribution | 4 |
Production
The Production sector accounts for 73% of the total methane emissions from the oil and natural gas industry. The chart below shows the distribution of the top emission sources in this sector.
| Emission Source | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Gathering and Boosting Stations | 26 |
| Pneumatic Controllers | 38 |
| Tanks | 7 |
| Chemical Injection Pumps | 5 |
| Liquids Unloading | 4 |
| Offshore Platforms | 4 |
| Completions and Workovers | 3 |
| Other | 13 |
Processing
The Processing sector accounts for 10% of the total methane emissions from the oil and natural gas industry. The chart below shows the distribution of the top emission sources in this sector.
| Emission Source | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Reciprocating Compressors | 49 |
| Centrifugal Compressors | 21 |
| Gas Engines | 20 |
| Blowdowns/Venting | 4 |
| Other | 6 |
Transmission
The Transmission and Storage sector accounts for 13% of the total methane emissions from the oil and natural gas industry. The chart below shows the distribution of the top emission sources in this sector.
| Emission Source | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Reciprocating Compressors | 35 |
| Station Fugitives | 11 |
| Engines | 10 |
| Pipelines | 10 |
| Station Venting | 9 |
| Centrifugal Compressors | 9 |
| Pneumatic Controllers | 5 |
| Other | 11 |
Distribution
The Distribution sector accounts for 4% of the total methane emissions from the oil and natural gas industry. The chart below shows the distribution of the top emission sources in this sector.
| Emission Source | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Mishaps (Dig-ins) | 15 |
| Residential | 13 |
| Mains - Unprotected Steel | 11 |
| Services - Unprotected Steel | 11 |
| Mains - Protected Steel | 10 |
| Commercial/Industry | 9 |
| Mains - Cast Iron | 8 |
| Other | 23 |
