Radionuclide Basics: Radon
 Radon (chemical symbol Rn) is an odorless, colorless, radioactive gas. It is the leading cause of lung cancer for U.S. residents who have never smoked.
Radon (chemical symbol Rn) is an odorless, colorless, radioactive gas. It is the leading cause of lung cancer for U.S. residents who have never smoked.
Radon is a radioactive gas. It comes from the natural decay of uranium and radium found in nearly all rocks and soils. Elevated radon levels have been found in every state. Radon is in the atmosphere and can also be found in ground water. The national average for radon in outdoor air is 0.4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L), while the average for indoor air is 1.3 pCi/L.
Radon can move up from the ground into buildings through openings in floors or walls that are in contact with the ground. Radon can accumulate in buildings and, over time, can pose a serious health hazard. Learn more about radon.
Any building can have high levels of radon, including new and old homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, office buildings and schools, and homes with or without basements. Testing is the only way to know if your home has elevated radon levels.
Radon gas can get into buildings through: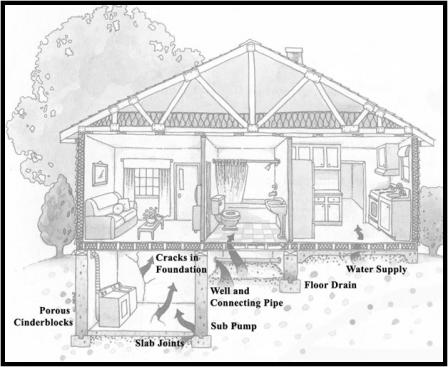
- Cracks in solid floors and walls
- Construction joints
- Gaps in suspended floors
- Gaps around service pipes
- Cavities inside walls
- The water supply
- Building materials
EPA recommends fixing your home when the radon level is at or above 4 pCi/L. Additionally, having your school tested for radon is something you may want to discuss with school officials.
Testing is inexpensive and easy — it should only take a few minutes of your time. Millions of Americans have already tested their homes for radon. If elevated levels are found, radon reduction systems work and they are cost effective. Even very high levels can be reduced to acceptable levels. Learn more about testing your home for radon.
EPA estimates that about 21,000 lung cancer deaths each year in the U.S. are radon-related. Exposure to radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. For never-smokers, it is the leading cause of lung cancer.
For most people, radon is the single greatest environmental source of radiation exposure. Learn more about radiation sources and doses, including radon. EPA recommends that all homes and schools be tested for radon. For smokers, the risk of lung cancer is heightened due to the combined effects of radon and smoking.