About Cuyahoga River AOC
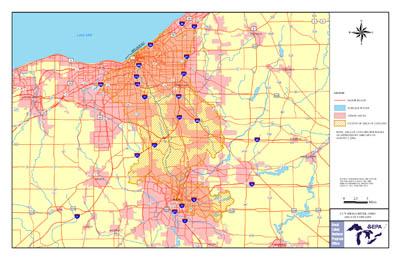 Boundary map of Cuyahoga River AOC
Boundary map of Cuyahoga River AOC
Location
The Cuyahoga River AOC is in northeastern Ohio, between Akron and Cleveland. The AOC is extensive. It includes:
- the lower 46.5 miles of the Cuyahoga River, starting at the head of the Gorge Dam pool in Akron/Cuyahoga Falls
- tributaries to the river (they drain 813 square miles of land in portions of six Ohio counties)
- the Cuyahoga Valley National Recreation Area (22 miles of river between Akron and Cleveland)
- ten miles of the Lake Erie shoreline, from the western border of Cleveland to Euclid Creek on the east, and tributaries to that portion of the shoreline
The boundary of the AOC was expanded in 2010 to include the Gorge Dam pool.
Environmental Problems in the Cuyahoga River AOC and their Causes
- poor water quality due to
- eutrophication
- toxic substances
- bacterial contamination
- loss of biodiversity due to
- water contamination
- habitat degradation
- sedimentation
- land use changes that have altered the river and its tributaries
- municipal and industrial discharges
- bank erosion
- commercial and residential development
- atmospheric deposition of contaminants
- hazardous waste disposal sites
- urban stormwater runoff
- and combined sewer overflows
- wastewater treatment plant bypasses
History
- the river was heavily polluted with oil, sludge, industrial waste, sewage and debris
- debris and oil floating on the river caught fire several times in the 20th century
- the river's discharge into Lake Erie caused damage that killed off the fish
Fires plagued the Cuyahoga River beginning in 1936 when a spark from a blow torch ignited floating debris and oils. The largest river fire in 1952 caused over $1 million in damage to boats and a riverfront office building. By the 1960s, the lower Cuyahoga River in Cleveland was used for waste disposal and was choked with debris, oils, sludge, industrial wastes and sewage. These pollutants were considered a major source of impact to Lake Erie, which was considered "dead" (devoid of fish) at the time.
On June 22, 1969, the Cuyahoga river caught fire and captured national attention. This incident led to important environmental legislation including the Clean Water Act. It also spurred the creation of federal and state environmental protection agencies.
In 1987, the International Joint Commission designated the Cuyahoga River an Area of Concern on the Great Lakes under the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement. In 1988, the Ohio Environmental Protection Agency appointed a 33-member planning committee to create the Remedial Action Plan for the AOC.
The Remedial Action Plan Stage I report was completed in 1992.
Beneficial Use Impairments
- Restrictions on Fish Consumption
- Degradation of Fish Populations
- Fish Tumors or Other Deformities
- Degradation of Benthos
- Restrictions on Navigational Dredging
- Eutrophication or Undesirable Algae
- Beach Closings (Recreational Contact)
- Public Access and Recreation Impairments
- Degradation of Aesthetics
- Loss of Fish Habitat
Restoring Cuyahoga River AOC (timeline) Substantial progress has been made on the impairments for the Cuyahoga River AOC.
