Scope 3 Inventory Guidance
On this page
Description of Scope 3 Emissions
Scope 3 emissions are the result of activities from assets not owned or controlled by the reporting organization, but that the organization indirectly impacts in its value chain. Scope 3 emissions include all sources not within an organization’s scope 1 and 2 boundary. The scope 3 emissions for one organization are the scope 1 and 2 emissions of another organization. Scope 3 emissions, also referred to as value chain emissions, often represent the majority of an organization’s total GHG emissions.
Scope 3 emissions fall within 15 categories, though not every category will be relevant to all organizations. Scope 3 emission sources include emissions both upstream and downstream of the organization’s activities.
According to GHG inventory guidance, quantification of scope 1 and 2 emissions are mandatory for organizations reporting and disclosing GHG emissions, while scope 3 emissions quantification is not required. However, more organizations are reaching into their value chain to understand the full GHG impact of their operations. In addition, because scope 3 emission sources may represent the majority of an organization’s GHG emissions, they often offer emissions reduction opportunities. Although these emissions are not under the organization’s control, the organization may be able to impact the activities that result in the emissions. The organization may also be able to influence its suppliers or choose which vendors to contract with based on their practices.
For a complete description of all scope 3 categories and quantification methods, see the World Resources Institute / World Business Council for Sustainable Development GHG Protocol Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard.
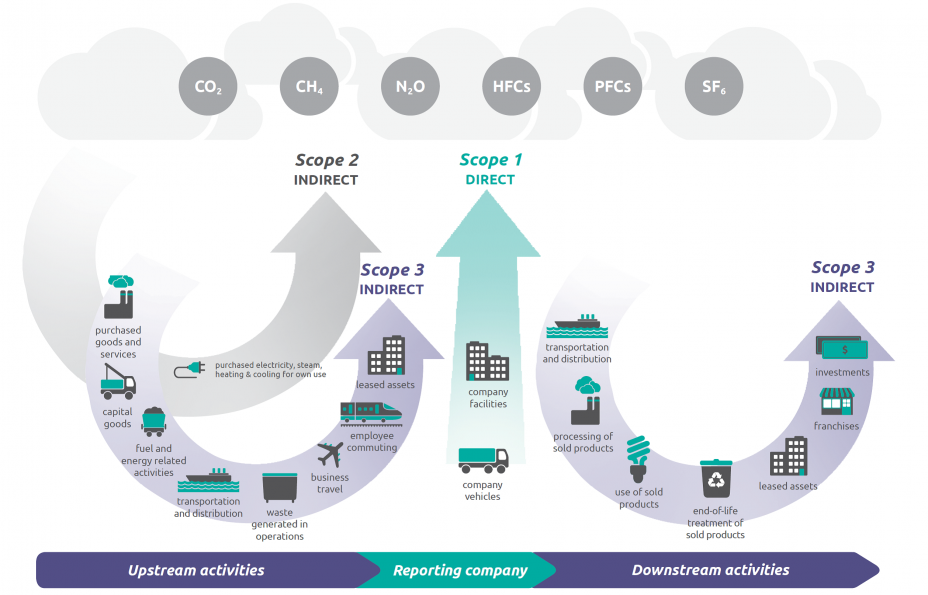
Source: WRI/WBCSD Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard, page 5.
Scope 3 Resources
The World Resources Institute / World Business Council for Sustainable Development GHG Protocol Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Accounting and Reporting Standard presents details on all scope 3 categories and requirements and guidance on reporting scope 3 emissions.
The GHG Protocol also provides the following additional scope 3 resources:
- Guidance for Calculating Scope 3 Emissions for each category, including guidance on required data, data collection methods, and quantification methods
- The Scope 3 Evaluator tool helps organizations screen scope 3 emissions categories to identifying focus areas
Depending on the source, scope 3 emissions can be quantified using either primary data specific to the activity within a company’s value chain, or using secondary data such as industry averages, proxy data, or other generic data. Primary data must often be collected directly from suppliers through a questionnaire or similar format.
The Carbon Trust provides a certification standard and framework for organizations that are measuring, managing, and reducing GHG emissions in their supply chain.
Scope 3 Emission Factors
The EPA Center for Corporate Climate Leadership currently provides certain scope 3 emission factors and is planning to expand the list. The sections below discuss the currently available factors, the factors to be included in the future, and how to apply scope 1 and 2 factors to calculate scope 3 emissions for certain categories. The categories listed are those defined in the GHG Protocol Scope 3 Standard.
Emission Factors Currently Available
The GHG Emission Factors Hub currently contains factors applicable to four scope 3 categories. Below is a list of emission sources and the location of the factors in the GHG Emission Factors Hub.
- Business Travel (Category 6)............................................Table 8, Business Travel
- Employee Commuting (Category 7)...................................Table 8, Business Travel1
- Upstream Transportation and Distribution (Category 4)......Table 9, Product Transport
- Downstream Transportation and Distribution (Category 9)..Table 9, Product Transport2
Emission Factors to be Included in the Future
Emissions Factors to assist with quantification in the following categories are under development and will be included in the next revision of the GHG Emission Factors Hub, expected at the end of 2016 or early 2017
- Purchased goods and services (Category 1)
- Capital goods (Category 2)
- Fuel- and energy-related activities (not included in scope 1 or scope 2) (Category 3)
- Waste generated in operations (Category 5)
Emission Source Categories Using Scope 1 and 2 Emission Factors
Some scope 3 categories do not require specific emission factors, because the emissions-generating activities have associated scope 1 and scope 2 factors already available in the GHG Emission Factors Hub. These sources include:
- Upstream leased assets (Category 8)
- Processing of sold products (Category 10)
- Use of sold products (Category 11)
- End-of-life treatment of sold products (Category 12)
- Downstream leased assets (Category 13)
- Franchises (Category 14)
- Investments (Category 15)
An organization may first define the GHG generating activity for each relevant source category, and then apply the appropriate factors for stationary combustion, mobile combustion, fugitive emissions, electricity, heat or steam from the GHG Emission Factors Hub.
For example, assume your organization produces electronic equipment. The downstream use of sold products (Category 11) may likely be a large source of emissions. In order to calculate emissions, estimate the lifetime electricity consumption (kWh) for all products sold in the reporting year. Then calculate emissions the same as for Scope 2 electricity, using eGRID emission factors. Depending on the data available for the location of product use, eGRID subregion or U.S. national average factors would be applied.
1These factors are applicable to employee commuting as well as business travel
2These factors are applicable to all transportation; upstream or downstream, product-related or not.
