Dynamometer Drive Schedules
On this page:
- EPA Vehicle Chassis Dynamometer Driving Schedules
- California EPA Air Resources Board Dynamometer Driving Schedules
- Economic Commission for Europe Dynamometer Operating Cycles
- Driving schedules specified in Japanese Technical Standards
- Vehicle Chassis Dynamometer Shift Schedule Formatting Guidance
This page provides the chassis dynamometer driving schedules and shift schedules used by EPA for vehicle emissions and fuel economy testing. This page also provides detailed information on those drive schedules in addition to technical information on drive schedules used by California, Europe, and Japan for reference.
The Code of Federal Regulations is the official source of EPA’s vehicle/engine certification test procedures.
Quick Graphic Review of Driving Schedules
EPA Vehicle Chassis Dynamometer Driving Schedules (DDS) - files contain tab delimited ASCII columns
|
The EPA Inspection and Maintenance (IM240) is often used for road-side vehicle testing. |
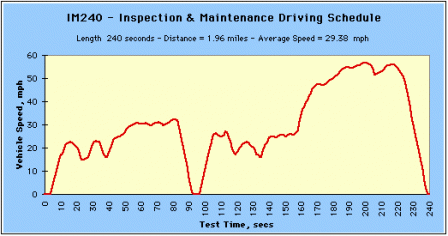 IM240 - Inspection and Maintenance Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) IM240 - Inspection and Maintenance Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
The EPA Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (UDDS) is commonly called the "LA4" or "the city test" and represents city driving conditions. It is used for light duty vehicle testing. The UN/ECE Regulation 53 refers to the EPA UDDS as the "Test Equivalent to the Type 1 Test (verifying emissions after a cold start)."
|
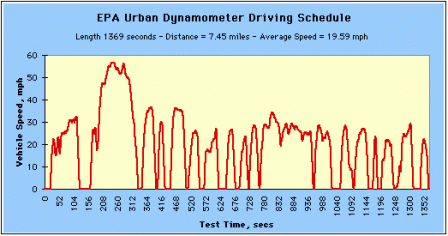 EPA Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) EPA Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
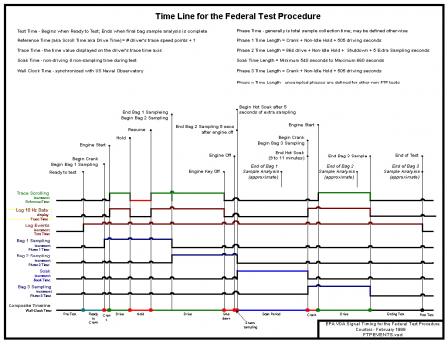
The Federal Test Procedure (FTP) is composed of the UDDS followed by the first 505 seconds of the UDDS. It is often called the EPA75. The dynamometer portion of the test procedure has a very complex timeline of events.
|
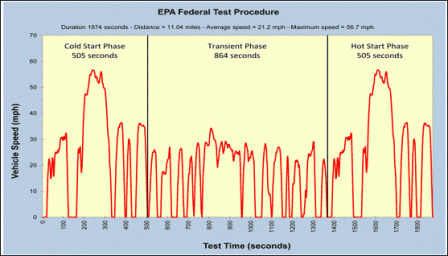 EPA Federal Test Procedure (Click image to see larger.) EPA Federal Test Procedure (Click image to see larger.)
|
|
The Highway Fuel Economy Driving Schedule (HWFET) represents highway driving conditions under 60 mph.
|
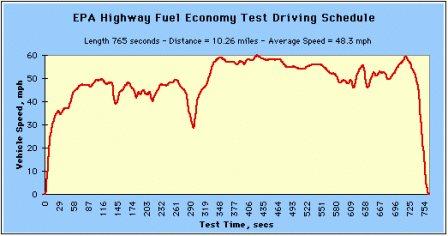 EPA Highway Fuel Economy Test Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) EPA Highway Fuel Economy Test Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
The New York City Cycle (NYCC) features low speed stop-and-go traffic conditions.
|
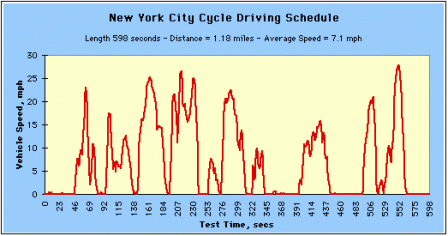 New York City Cycle Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) New York City Cycle Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
The US06 is a high acceleration aggressive driving schedule that is often identified as the "Supplemental FTP" driving schedule.
|
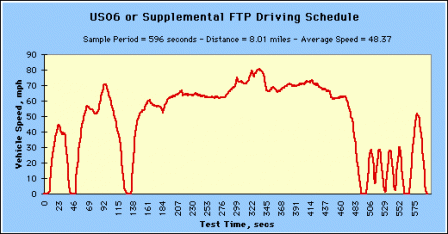 US06 or Supplemental FTP Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) US06 or Supplemental FTP Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
The SC03 is the Air Conditioning "Supplemental FTP" driving schedule.
|
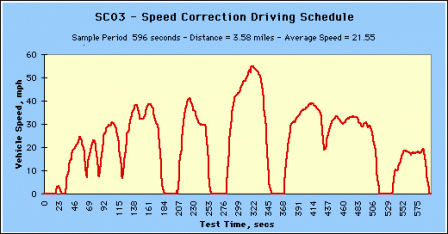 SC03 - Speed Correction Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) SC03 - Speed Correction Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
The EPA Heavy Duty Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule is for heavy duty vehicle testing. Be careful! Do not confuse it with the usual UDDS for light duty vehicle testing. |
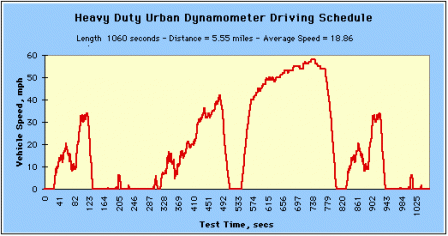 Heavy Duty Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) Heavy Duty Urban Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
Vehicle Chassis Dynamometer Shift Schedule Formatting Guidance
- Graphics images and one hertz text files for the driver's traces for the FTP, HWFET and other drive schedules are available on this page.
- 10 Hertz Text Files for some of traces are also available on this page.
- Sample Formatting Tool(1 pg, 42 K) for putting shift schedule data into the CFEIS shift schedule format.
- Draft Guidance for submission of shift schedules to the NVFEL(1 pg, 5 K) .
- Example EPA 5 speed FTP, HWFET and US06 shift schedules are in the following files.
- EPA 5 speed FTP(1 pg, 4 K)
- EPA 5 speed HWFET(1 pg, 917 B)
- US06 shift schedules(1 pg, 3 K)
California EPA Air Resources Board Dynamometer Driving Schedules
|
The Air Resources Board LA92 Dynamometer Driving Schedule, often called the Unified driving schedule, was developed as an emission inventory improvement tool. Compared to the FTP, the LA92 has a higher top speed, a higher average speed, less idle time, fewer stops per mile, and a higher maximum rate of acceleration.
|
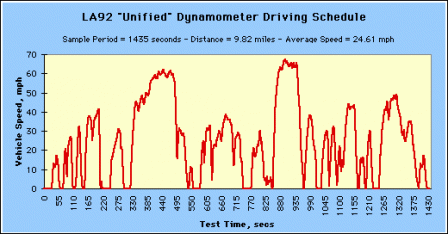 LA92 "Unified" Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) LA92 "Unified" Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
The LA92Short contains the first 969 seconds of the LA92 (Unified) Dynamometer Driving Schedule. |
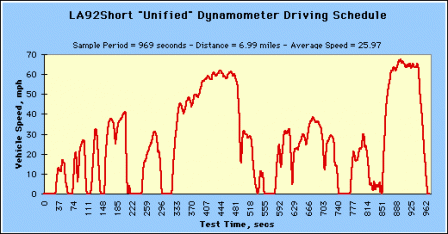 LA92Short "Unified" Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) LA92Short "Unified" Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
For more information, leave the U.S. EPA web site and go to the California EPA Air Resources Board.Exit
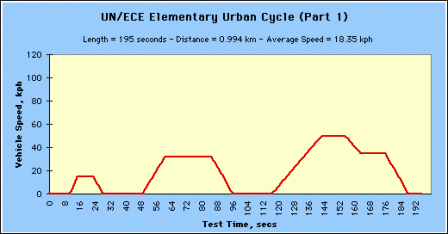
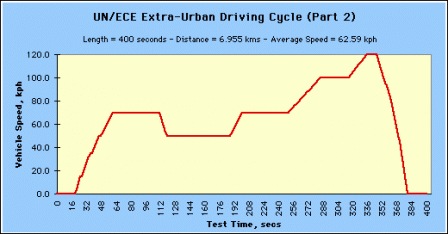
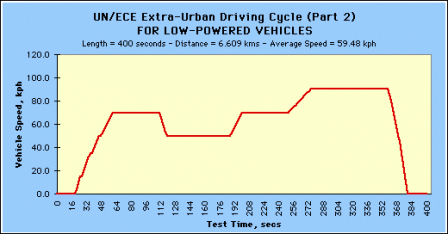
Economic Commission for Europe Dynamometer Operating Cycles - Official guidance is found in the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UN/ECE) WP.29 1958 Agreement and its Addenda. Guidance is specifically found in Regulation 83 of the Regulations for the Construction of Vehicles.
Driving schedules specified in Japanese Technical Standards - Official guidance is found in the Japanese Industrial Safety and Health Association (JISHA) Technical Standards. The 11 Mode and 13 Mode driving schedules are not yet available for posting. Technical Guidances Include:
- Rev. 11-4-28 Technical Standard for 10¥15-Mode Exhaust Emission Measurement for Gasoline-Fueled Motor Vehicles (Jisha 899, 1983);
- Rev. 11-4-29 Technical Standard for 10-Mode and 11-Mode Exhaust Emission Measurement for Gasoline-Fueled Motor Vehicles (Jisha 899, 1983);
- Rev. 11-4-30 Technical Standard for 13-Mode Exhaust Emission Measurement for Gasoline-Fueled Motor Vehicles (Jisha 899, 1983);
- Rev. 11-4-31 Technical Standard for 10.15-Mode Exhaust Emission Measurement for Diesel-Powered Motor Vehicles (Jisha 899, 1983);
- Rev. 11-4-32 Technical Standard for 10-Mode Exhaust Emission Measurement for Diesel-Powered Motor Vehicles (Jisha 899, 1983);
- Rev. TRIAS 5-2-1990 10-Mode Fuel Economy Test Procedure for Gasoline-Fueled Motor Vehicles; and
- Rev. TRIAS 5-3-1991 Technical Standard for 10.15- Fuel Economy Test Procedure for Gasoline-Fueled Motor Vehicles.
|
The Japanese 10 Mode Cycle is used as a component of the total driving schedule for the 10.15 Mode Exhaust Measurement and Fuel Economy Test Procedures.
|
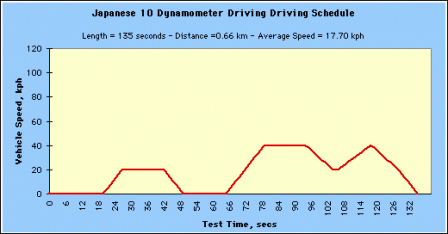 Japanese 10 Dynamometer Driving Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) Japanese 10 Dynamometer Driving Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
The Japanese 15 Mode Cycle is used as a component of the total driving schedule for the 10.15 Mode Exhaust Measurement and Fuel Economy Test Procedures.
|
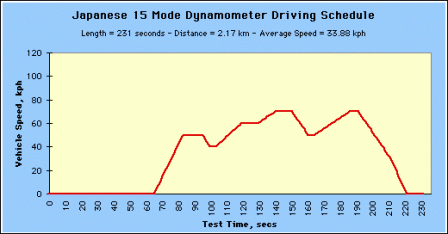 Japanese 15 Mode Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) Japanese 15 Mode Dynamometer Driving Schedule (Click image to see larger.) |
|
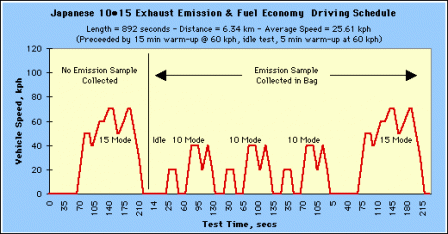
The Japanese 10.15 Mode Driving Schedule for Exhaust Measurement and Fuel Economy Test Procedures are specified in Jisha Technical Standards (Jisha 899, 1983). |
|