The Mystic River Watershed Initiative
- Meetings and Events
- Report Card
- Accomplishments to Date
- Hurd Field Porous Pavement Project
- A Timeline of Work in the Mystic
- Photo Galleries
The Mystic River Watershed Initiative is a collaborative effort with a goal to improve water quality and environmental conditions as well as create and protect open space and public access to the Mystic River and its tributaries through safe public pathways and access points. The Initiative is guided by a steering committee composed of 22 organizations including not-for-profit community groups, local, state, and federal governmental agencies. To hear thoughts, perspectives, and insight from some of the not-for-profit and municipal Steering Committee members, play video below.
Mystic River Watershed Initiative Video, May 2010
- The Mystic River Watershed Initiative
- The Steering Committee Purpose and Structure
- The Steering Committee Mission and Priorities
Meetings and Events
You will need Adobe Reader to view some of the files on this page. See EPA's About PDF page to learn more.
Upcoming Meetings
Mystic River Watershed Initiative Steering Committee Meeting
Date: January 26, 2017
Time: 9:30-12:00pm
NEW LOCATION: Watertown Town Hall, 149 Main St, Watertown, MA 02472
Past Meetings Archive
Steering Committee
Mystic River Watershed Initiative Steering Committee Meeting, October 13, 2016
Location: Massachusetts Dept. of Environmental Protection - 205 Lowell St, Wilmington, MA 01887
- Agenda (PDF) (2 pp, 196 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (6 pp, 370 K)
Open Space Subcommittee Meeting, September 29, 2016
Location: Green Roots Chelsea: 227 Marginal St. Suite 1 Chelsea
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 279 K)
Mystic River Watershed Initiative Steering Committee Meeting, June 9, 2016
Location: City of Everett, 484 Broadway, Everett, MA
Mystic River Federal Partners Grant Information Event, March 31, 2016
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 286 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, March 10, 2016
Location: Arlington Town Hall, 2nd Floor Lyons Hearing Room, 730 Massachusetts Ave., Arlington, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 106 K)
Open Space Subcommittee Meeting, February 11, 2016
Location: Century Bank, 400 Mystic Ave., Medford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 286 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, December 10, 2015
Location: House Member's Lounge, Massachusetts State House, 24 Beacon St., Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 149 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (5 pp, 313 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, September 10, 2015
Location: Chelsea Collaborative, 318 Broadway, Chelsea, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 250 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (6 pp, 317 K)
Mystic River Watershed Federal Partnership Annual Call, September 1, 2015
- Agenda (PDF) (2 pp, 116 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (4 pp, 351 K)
MA DCR's Mystic Master Plan Presentation, June 18, 2015
Location: EPA Region 1 - Leighton Hall, 1st Floor, 5 Post Office Sq. Boston, MA
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (5 pp, 413 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, June 4, 2015
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 283 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (7 pp, 431 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, April 16, 2015
Location: Teleconference
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 206 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (3 pp, 312 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, December 11, 2014
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 206 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (6 pp, 424 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, June 19, 2014
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 206 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (3 pp, 308 K)
- Massport Presentation Exit
Steering Committee Meeting, March 6, 2014
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (2 pp, 109 K)
- Meeting Report (PDF) (3 pp, 118 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, September 25, 2013
Location: Preotle, Lane & Associates, Ltd., River's Edge Office Park, 200 River's Edge Drive, Medford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 234 K)
- Meeting Report (PDF) (3 pp, 26 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, June 12, 2013
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 94 K)
- Meeting Report (PDF) (9 pp, 62 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, March 28, 2013
Location: River's Edge, 200 River's Edge Drive, Medford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (2 pp, 98 K)
- Meeting Report (PDF) (5 pp, 61 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, December 5, 2012
Location: Arlington Town Hall, 730 Mass Avenue, Arlington, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (2 pp, 97 K)
- Meeting Minutes (PDF) (5 pp, 42 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, September 5, 2012
Location: Winchester Town Hall, 71 Mount Vernon Street, Winchester, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 40 K)
- Meeting Report (PDF) (4 pp, 35 K)
Open Space Sub-Group Meeting, July 26, 2012
Location: Draw 7 Park, Somerville, MA (Back-up location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA)
Steering Committee Meeting, June 6, 2012
Location: MassDEP Northeast Regional Office, 205B Lowell Street, Wilmington, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 52 K)
- Meeting Report (PDF) (5 pp, 80 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, March 7, 2012
Location: Pfizer Building, 200 Cambridge Park Drive, Cambridge MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 138 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (5 pp, 217 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, December 7, 2011
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 106 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (6 pp, 319 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, September 7, 2011
Location: Conservation Law Foundation, 62 Summer Street, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 98 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (10 pp, 245K)
Steering Committee Meeting, May 18, 2011
Location: Massachusetts State House, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 47 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (11 pp, 70 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Open Space Group - Conference Call, April 26, 2011
- Conference Call Notes (PDF) (3 pp, 99 K)
Water Quality Subgroup Meeting, April 11, 2011
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (4 pp, 97 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, February 16, 2011
Location: MAPC, 60 Temple Place, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 11 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (9 pp, 118 K)
Water Quality Subgroup Meeting, January 24, 2011
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (2 pp, 64 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Water Quality Group, December 8, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (2 pp, 64 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, November 17, 2010
Location: Tuft's Boathouse, 300 River's Edge Drive, Medford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 11 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (10 pp, 70 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Open Space Group, November 8, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (4 pp, 33 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Open Space Group, October 4, 2010
Location: Groundwork Somerville, Somerville, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (3 pp, 24 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Water Quality Group, September 29, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (3 pp, 46 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, September 15, 2010
Location: Delta Dental Building, Schrafft's Complex, 465 Medford Street, Charlestown, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 11 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (9 pp, 64 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, July 21, 2010
Location: Whip Hill Park, Perkins Street, Stoneham, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (10 pp, 54 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Open Space Group, July 7, 2010
Location: Pfizer, 25 Cambridge Park Drive, Cambridge, MA
- Agenda and Directions (PDF) (1 pg, 14 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (7 pp, 50 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Water Quality Group, June 14, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 11 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (6 pp, 41 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Open Space Group, May 26, 2010
Location: Pfizer, 200 Cambridge Park Drive, Cambridge, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 11 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (5 pp, 32 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, Water Quality Group, May 12, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (6 pp, 36 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, March 31, 2010
Location: Century Bank, 400 Mystic Avenue, Medford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 12 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (12 pp, 70 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, January 20, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 90 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (9 pp, 208 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, November 18, 2009
Location: Chelsea City Hall, 500 Broadway, Chelsea, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 89 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (9 pp, 59 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, September 16, 2009
Location: EPA New England, 1 Congress Street, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 96 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (8 pp, 262 K)
Steering Committee Meeting, July 15, 2009
Location: Century Bank, 400 Mystic Avenue, Medford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 81 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (6 pp, 242 K)
NAWCA Grant Writing Workshop, June 9, 2009
Location: Chelsea City Hall, 500 Broadway, Chelsea, MA
Steering Committee Meeting, May 20, 2009
Location: Town Hall in the Winchester Room, Winchester, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 87 K)
- Flip Chart Notes (PDF) (5 pp, 172 K)
First Mystic River Watershed Steering Committee Meeting, March 11, 2009
Locaton: JFK Federal Building, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 101 K)
- Flip Chart Notes (PDF) (4 pp, 165 K)
Pre-Steering Committee Meetings
Municipal
Illicit Discharge Detection and Elimination (IDDE) Program Workshop for Mystic Municipalities
Location: Lexington DPW: 201 Bedford St., Lexington, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 250 K)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, November 25, 2014
Location: Woburn Senior Center, 144 School St, Woburn, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 143 K)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, November 15, 2012
Location: Arlington Town Hall, 730 Mass Avenue, Arlington, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 10 K)
- Presentation: Design and Contruction of a Porous Asphalt Stormwater BMP Retrofit - An EPA Education and Outreach Project (PDF) (31 pp, 7 MB)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, September 22, 2011
Location: Everett City Hall, 484 Broadway, Everett, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 11 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (7 pp, 59 K)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, July 20, 2011
Location: Woburn Senior Center, 144 School Street, Woburn, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 10 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (9 pp, 67 K)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, October 28, 2010
Location: Winchester Town Hall, Winchester, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 10 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (4 pp, 44 K)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, July 29, 2010
Location: Reading Public Library, 64 Middlesex Avenue, Reading, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 12 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (6 pp, 38 K)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, April 29, 2010
Location: Senior Center, 144 School Street, Woburn, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (5 pp, 37 K)
Municipal Subcommittee Meeting, January 14, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 86 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (3 pp, 37 K)
Science
Water Quality Subcommittee Meeting, March 3, 2016
Location: EPA New England, Mt. Madison Room (15th Floor), 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 202 K)
Science Forum, April 9, 2015
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 383 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (8 pp, 438 K)
Water Quality Subcommittee Meeting, March 19, 2015
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 206 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (2 pp, 298 K)
Water Quality Subcommittee Meeting, November 18, 2014
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 235 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (3 pp, 304 K)
Water Quality Subcommittee Meeting, July 15, 2014
Location: EPA New England, Mt. Madison Room (15th Floor), 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 186 K)
- Meeting Summary (PDF) (5 pp, 343 K)
Annual Mystic River Water Quality Forum, January 24, 2013
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 17 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (6 pp, 42 K)
- Non-EPA Presentations Exit
Mystic River Watershed Water Quality Sub-Group Meeting, July 25, 2012
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
Science Subcommittee Meeting, Water Quality Workgroup, May 11, 2011
Location: EPA New England Regional Laboratory, 11 Technology Drive, Chelmsford, MA
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (5 pp, 248 K)
Annual Mystic River Water Quality Forum, January 11, 2011
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 19 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (19 pp, 108 K)
Science Subcommittee Meeting, Water Quality Workgroup, November 3, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 12 K)
Science Subcommittee Meeting, Water Quality Workgroup, May 4, 2010
Location: EPA New England Regional Laboratory, 11 Technology Drive, Chelmsford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 38 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (3 pp, 25 K)
Water Quality Science Subcommittee Meeting, January 7, 2010
Location: EPA New England, 5 Post Office Square, Boston, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 14 K)
- Meeting Notes (PDF) (12 pp, 250 K)
- Presentations
- EPA Stormwater Monitoring and Research Effort Summary (PDF) (21 pp, 2 MB)
- EPA Superfund Sites Within the Upper Mystic River Watershed - Olin Chemical Superfund Site Wilmington, MA (PDF) (13 pp, 1 MB)
- EPA Presentation on Industri-plex Superfund Site Operable Unit 2 (OU2) Remedy (PDF) (19 pp, 3 MB)
- Non-EPA Presentations Exit
Water Quality Science Committee Meeting, February 11, 2009
Location: EPA New England, 1 Congress Street, Boston, MA
- Agenda and Meeting Notes: Water Quality Science Committee Meeting February 11, 2009 (PDF) (13 pp, 213 K)
Science Subcomittee
Summit
EPA New England would like to thank everyone that participated in the Mystic River Watershed Summit, held April 10, 2008 in Boston. Over 170 people attended the summit and we are quite pleased with all the energy and enthusiasm that was displayed at the summit. We look forward to working with the Mystic watershed groups and communities to restore water quality in the watershed. Revitalizing the Mystic will be quite a challenge, but forming strong partnerships is the first step toward reaching our common goals.
The draft meeting notes from the Summit have been posted on this web site. Numerous conference calls were held over the summer to finish up discussions and review our typed notes from the breakout sessions. The goal of these calls was to review and refine the meeting notes and further develop actions and priorities.
As an outgrowth of the Summit, EPA New England is spearheading a collaborative effort to revitalize the Mystic with federal, state, and local partners. We are hoping to work with a formal steering committee to implement short- and long-term water quality goals that will be established early 2009. This winter, EPA New England hopes to co-sponsor a science committee meeting, which will be a forum to provide opportunity for researchers to share information on their projects within the watershed.
Mystic River Summit Notes:
Flooding
The flooding group met at the summit and discussed several opportunities for additional communication between agencies and municipalities during a flood event. Currently, DCR, Winchester and Woburn work together during a flood event, but there is opportunity for additional collaboration with the Arlington-Belmont-Cambridge flooding group and the City of Somerville. There remains difficulty discussing flooding as it relates to water quality. A brainstorming session was summarized into several types of actions that could improve flood conditions and reduce flooding in the watershed. They are: maintenance actions, regional communication/collaboration, and updated land use policies.
Land Use and Connecting people to the River
The land use group identified several areas where action is needed in the watershed. The group tackled issues such as changing land use and its impact on the river, reconnecting people to the river, and fish advisories. The group determined that access and redevelopment are needed in designated port areas; that enforcement of permits and regulations at the federal and state level should be a priority; that there is a need to add and connect bike paths, multiuse paths, and walkways in the watershed; that all new development and redevelopment should be environmentally responsible; and that public access to the river is still a big issue. This group recommended public education campaigns for many of these issues as well as for subsistence fishing, for which there is a watershed-wide advisory.
Bacteria & Stormwater
One of the biggest outcomes of the bacteria group is the recommendation to add a Science Committee to the Initiative structure. The Science Committee will provide a venue once or twice a year for scientists to share research and information about water quality in the watershed. The committee may also be accessed for recommendations or scientific advice in future steering committee actions. Other follow-ups suggested from the session are to reduce the inflow from CSOs and SSOs, to increase monitoring thru increased funding and support for monitoring, and to reduce and eliminate stormwater and illicit connections in the watershed.
Industrial Contaminants
The Industrial Contaminants group has continued to focus on expanding recreational uses in the watershed by prioritizing key sites (Mill Creek, Malden River, Spy Pond, and Upper Mystic Lake). These locations were selected from an initial list of ten sites* based on their geographic distribution, potential for improvement, and diversity and number of people who will benefit from their improvement. This is still a draft list, as the group intends to vet these to a wider audience. Since July, MyRWA and EPA have conducted water quality studies, collecting more than 500 samples from throughout the watershed. USGS has also conducted sediment quality monitoring. Data from these studies are being used to identify and eliminate both point and non-point sources of pollution in areas that can provide greater recreation to residents.
*The original list of sites included:
- Mill Creek, Chelsea
- Urban Wild, Chelsea
- Admirals Hill, Chelsea
- Spy Pond, Arlington
- Sandy Beach, Winchester
- Cross St. Swimming Area, Winchester
- Blessing of the Bay Boathouse, Somerville
- Constitution Beach, East Boston
- Tufts University Boathouse, Malden
- Horn Pond, Woburn
- Open Mike (PDF) (2 pp, 13 K)
- Executive Summary for Changing Land Use & Impacts (PDF) (2 pp, 24 K)
- Changing Land Use & Impacts on the Mystic River Breakout Session Notes (PDF) (5 pp, 39 K)
- Flooding Breakout Group Notes (PDF) (4 pp, 26 K)
- Industrial Contaminants Breakout Session Notes (PDF) (2 pp, 14 K)
- Bacteria & Stormwater Breakout Session (PDF) (5 pp, 42 K)
Business
Business Subcommittee Meeting, September 22, 2010
Location: Century Bank, Medford, MA
- Agenda (PDF) (1 pg, 11 K)
Mystic River Watershed Report Cards
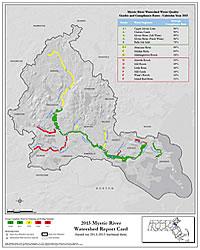 EPA produced a watershed map for 2015 that identifies areas in the watershed where water quality is generally good and generally needs improvement.
EPA produced a watershed map for 2015 that identifies areas in the watershed where water quality is generally good and generally needs improvement.
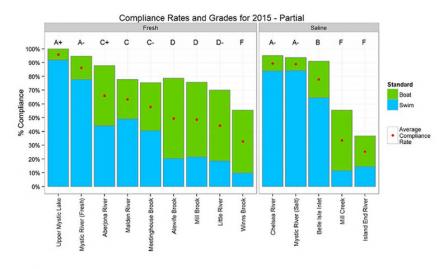
EPA has been assigning a report card grade for the Mystic River Watershed since calendar year 2006. For the past two years, in coordination with the Mystic River Watershed Association (MyRWA), EPA has utilized an enhanced, more locally-specific analysis of water quality in the Mystic River Watershed to illuminate environmental conditions for the public. Instead of one grade for the entire watershed, EPA and MyRWA now issue grades for each segment of the watershed, totaling 14 separate stretches of river and its tributaries.
 View a larger version of this image.
View a larger version of this image.
Figure 1 - Developed and provided by MyRWA.
For more information on how the grades are assigned please read the Frequently Asked Questions and review the data on MyRWA's Website Exit.
Grading Criteria Prior to 2014
When assessing water quality to assign a grade to the Mystic River Watershed prior to 2014, EPA used an average between the overall percentages that water quality met the state criteria for swimming and boating (for 2013, it was 66%) as well as qualitative criteria that are similar to those developed for the Charles River Initiative, as follows:
A - met swimming and boating standards nearly all of the time
B - met swimming and boating standards most of the time
C - met swimming standards some of the time, and boating standards most of the time
D - met swimming and boating standards some of the time
F - fail swimming and boating standards most of the time
| Year | Grade | Overall* | Dry* | Wet* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boating | Swimming | Boating | Swimming | Boating | Swimming | ||
| 2013 | D | 83% | 49% | 88% | 51% | 67% | 42% |
| 2012 | D | 75% | 47% | 84% | 58% | 45% | 14% |
| 2011 | D | 87% | 46% | 93% | 54% | 69% | 25% |
| 2010 | D- | 70% | 28% | 72% | 26% | 63% | 33% |
| 2009 | C- | 93% | 57% | 93% | 51% | 90% | 75% |
| 2008 | C- | 90% | 59% | 93% | 64% | 81% | 43% |
| 2007 | D | 68% | 46% | 63% | 45% | 83% | 50% |
| 2006 | D | 80% | 52% | 93% | 59% | 41% | 30% |
| 2005** | 85% | 56% | 90% | 64% | 69% | 31% | |
| 2004** | 79% | 52% | 85% | 59% | 61% | 59% | |
| 2003** | 81% | 55% | 81% | 53% | 81% | 62% | |
| *Figures represent the percentage of time that state bacterial standards are met. **The Mystic River Watershed did not receive formal grades for the years 2003 - 2005. |
|||||||
Mystic River in the News
- 5/31/16
Localized Mystic River Report Card Shows Specific Information about Water Quality - 7/18/15
New Grading System for Mystic River Watershed Gives Public Better Localized Information - 12/18/2014
EPA Announces 2013 Report Card Grade for the Mystic River Watershed - 08/19/2014
EPA Awards $120,000 in Urban Waters grants to Revitalize Mystic River Watershed - 08/07/2013
EPA Announces 2012 Report Card grades for the lower Charles River and the Mystic River Watershed - 05/10/2013
Federal Agencies Expand Urban Waterway Revitalization Efforts in Communities Across the Nation - 08/23/2012
Settlement Requires Boston Water and Sewer Commission to Remedy Sewer and Stormwater Discharges - 08/22/2012
Clean Water Act Settlement Ensures That Boston Racetrack Addresses Wastewater and Stormwater Discharges - 05/20/2012
Mystic River Water Quality Receives a "D" - Ongoing efforts, analysis highlight problem areas - 10/14/2011
ExxonMobil Addresses Stormwater at Everett Terminal – Better Water Quality in Mystic and Island End Rivers Will Result - 05/15/2011
Mystic River Water Quality Score Downgraded to D- Despite ongoing efforts, analysis shows more work needed - 05/16/2010
Mystic River Scores C- : Good Progress Underway - 05/02/2009
Report Card for Mystic River: "C-" with Notable Improvement - 10/17/2008
Equipment Loans Help New England Volunteers Collect Water Quality Info - 5/15/2008
Suffolk Downs Race Course Ordered to Reduce Bacterial Waste in Stormwater - 04/10/2008
EPA Mystic River Report Card: "D" – Room for Improvement – Help Is On the Way - 04/17/2007
EPA Kicks Off Major Effort to Improve Conditions of Mystic River Watershed - 02/26/2007
Everett, Mass. Metal Finisher Fined and Settles Environmental Violations - 10/30/2006
Massachusetts Celebrates World Water Monitoring Day - 07/12/2006
Mass. Recycling Facility Facing Fines for Clean Water Violations - 03/10/2004
$1.4 Million Environmental Settlement With MBTA Brings Clean Air and Water Benefits to Boston: Settlement Stems from Bus Idling and Water Pollution Violations - 12/03/2001
EPA Awards $363,257 Grant to Somerville for Mystic River Project
Accomplishments to Date
Ongoing Accomplishments
- Real-Time Monitoring
EPA is conducting real-time monitoring using a remote sensing buoy near the Blessing of the Bay Boathouse to track water quality conditions and cyanobacteria blooms for the fourth year in a row.
- Stopping Illicit Connections
EPA enforcement efforts have stopped over 14,000 gallons per day of sewage from being discharged to the watershed through illicit connections (a 4,000 gallon increase since 2009).
- Providing Monitoring Equipment
EPA Region 1 has loaned over $14,000 worth of monitoring equipment to the Mystic River Watershed Association in support of baseline and hot spot monitoring programs, as well as microbiology assistance. The agency has analyzed over 2,000 samples from the Mystic River Watershed for E. coli and Enterococcus bacteria.
- Steering Committee Efforts
The Steering Committee has formed subcommittees to focus on the mission and priorities of the Steering Committee: to help establish strategic direction and priorities as well as to recommend and promote key projects and actions needed to improve environmental conditions in the Mystic River Watershed.
2013
- Urban Waters Academic Forum Jan 2013
EPA organized the Urban Waters Academic Forum to bring together academic professionals to explore areas for future collaboration on urban water issues in the Mystic River, Neponset River, and Charles River Watersheds, with a focus on the challenges of stormwater and nutrient pollution in these urbanized watersheds.
- Mystic River Water Quality Science Forum Jan 2013
EPA Region 1 hosted this forum to update stakeholders on water quality and environmental conditions, learn from success stories, and foster discussion on what action will be needed to increase publicity and funding in order to achieve goals in the coming year.
2012
- Enforcement Litigation
As a result of EPA enforcement action under the Clean Water Act, Sterling Suffolk Racecourse LLC (Suffolk Downs) was required to pay a civil penalty of $1.25 million and will perform three environmental projects that provide water quality monitoring and protection. This includes implementing green infrastructure and low impact development techniques to address stormwater discharges from the racetrack and maintenance areas of the facility.
- Sterling Suffolk Racecourse LLC Clean Water Act Settlement
- Clean Water Act Settlement Ensures That Boston Racetrack Addresses Wastewater and Stormwater Discharges
- Greening Boston's Infrastructure
As a result of a consent decree between EPA and the Boston Water and Sewer Commission (BWSC), BWSC was required to implement extensive remedial measures to minimize the discharge of sewage and other pollutants into the water bodies in and around Boston, including the Mystic River. This settlement will produce lasting benefits for the people of Boston, incorporating green infrastructure, low impact development, and other controls that will help reduce harmful discharges and protect the environment.
- Arlington Porous Pavement Project
EPA Region 1 used regional and national funds to construct a porous asphalt stormwater best management practice (BMP) retrofit in Arlington, MA, as part of an education and outreach project under the Clean Water Act. The Hurd Field, Arlington, MA, parking lot was designed and constructed over the course of 2012 and completed in September of 2012. Under an agreement with the Town of Arlington, the Town will maintain the parking lot and EPA and the Town will observe the BMP over time to better understand the performance and longevity of this BMP technology. EPA will use the project as an opportunity to inform practitioners as to the overall efficacy of porous asphalt for stormwater control in urban areas. In addition, the project will help to improve water quality in Mill Brook, an impaired waterbody in the Mystic River Watershed. View a video detailing the project.
- Supporting the City of Chelsea
EPA Region 1 provided technical assistance to complete a detailed review of the City of Chelsea's existing codes and ordinances with specific recommendations for: incorporating green infrastructure in the City; a technical support documents summarizing the range of GI techniques (including costs, operation, and maintenance, etc.) that may best be employed considering the City's constrained urban areas and class C/D soils; and a convenient informational brochure summarizing pertinent information on incorporating GI within the City. Also, this led to a December 2012 information workshop for the City's officials and board to better understand GI.
2011
- Agreement with UMass Boston
EPA Region 1 signed an MOU with UMass Boston for the region's Urban Waters/Mystic River University Collaborative. EPA hired a co-op student in 2010 and is working closely with UMass Boston to support its urban waters/Mystic River Watershed efforts, beach, nonpoint source and other programs.
- Improved Permitting of ExxonMobil
Two years after the settlement with ExxonMobil, EPA issued a modified permit that incorporated the substantial improvements ExxonMobil made to the stormwater management system at its Everett Terminal. The facility upgrades greatly improve the capacity of the stormwater system to collect, store and treat large storm events and provide advanced treatment for residual contaminated groundwater that infiltrates into the stormwater collection system.
- Stormwater Workshop April 2011
EPA Region 1 held a stormwater workshop in Chelsea, MA to review the provisions of the draft North Coastal small MS4 NPDES permit and low impact development techniques.
2010
- Consent Decree in Revere
Under the terms of a Consent Decree lodged in federal court, Mass EPA reached a settlement with the City of Revere to spend approximately $50 million on infrastructure improvements. This will be used to significantly reduce illegal discharges of raw sewage overflows into the Mystic River Watershed from its wastewater collection system and separate storm sewer system.
- Financial Support to Mystic River Watershed Association
EPA Region 1 awarded $9,000 to the Mystic River Watershed Association and community partners to support stormwater education and outreach efforts in the watershed.
2009
- ExxonMobil Litigation
The Mystic River Watershed received grant funding derived from the criminal sentence imposed in the federal Clean Water Act case against ExxonMobil Pipeline Company. As a result of this case, the Massachusetts Environmental Trust issued $1 million in grants and the North American Wetlands Conservation Trust issued $1,663,150 in grants all for environmental projects to the Mystic River and Chelsea Creek.
2008
- Administrative Order to Reduce Bacterial Waste
EPA ordered Suffolk Downs to immediately cease discharging pollutants being discharged to Sales Creek, a tributary in the Mystic River Watershed. Suffolk now routinely inspects its facility for discharges to Sales Creek and the adjacent wetland and collects limited dry- and wet-weather samples from its outfalls.
- Mystic River Watershed Summit April 2008
EPA Region 1 held a Mystic River Watershed Summit that focused on Flooding, Industrial Contaminants, Bacteria and Stormwater, and Reconnecting people to the river. The summit was attended by over 150 people.
2001
- Funds for Real-Time Monitoring
EPA Region 1 awarded $363,257 to Somerville to develop a state-of-the-art system that can predict, assess and report the Mystic River's water quality in real time. Residents will be able to check water quality indicators online or by flags along the river to determine whether sewer overflows and runoff have made the water unsafe for recreational use.
Mystic River Timeline
-
2005 - 2006 - Information Requests Issued: EPA issued information requests to five municipalities in the lower watershed based on baseline data collected by MyRWA which indicated high bacteria levels in the Mystic and tributaries. Information Requests provided more data and led to the issuance of several orders in later years.
-
2007 - First Annual Water Quality Report Card: The Mystic receives a D as its first Water Quality Report Card grade for calendar year 2006. Grades and related press releases for subsequent years can be seen at: /mysticriver/mystic-river-watershed-initiative#ReportCard .
-
2008 - The Mystic River Watershed Initiative: EPA launches the Mystic River Watershed Initiative in order to improve water quality and public access to open space in the watershed.
-
2007 - 2009 - Administrative Orders: EPA issues Administrative Orders to several lower Mystic River communities to remove illicit discharges from the storm drain system discharging to the Mystic River and its tributaries.
-
2008 - Administrative Order to Suffolk Downs: EPA ordered Suffolk Downs to immediately cease discharging pollutants being discharged to Sales Creek, a tributary in the Mystic River Watershed. Suffolk now routinely inspects its facility for discharges to Sales Creek and the adjacent wetland and collects limited dry- and wet-weather samples from its outfalls.
-
2009 - Exxon Mobil Litigation: The Mystic River Watershed received grant funding derived from the criminal sentence imposed in the federal Clean Water Act case against ExxonMobil Pipeline Company. As a result of this case, the Massachusetts Environmental Trust issued $1 million in grants and the North American Wetlands Conservation Trust issued $1,663,150 in grants all for environmental projects to the Mystic River and Chelsea Creek.
-
2009 - Mystic River Watershed Steering Committee: The Steering Committee was created to allow environmental advocates, state and federal regulators, and business and municipal leaders to work collaboratively to promote actions that will improve environmental conditions throughout the watershed. The Committee is focusing on restoring and protecting water quality, wildlife and its habitats, while also protecting and creating open public spaces for safe public access to the waterfront.
-
2010 - City of Revere Consent Decree: EPA and the Department of Justice negotiate a Consent Decree with the City of Revere to address Sanitary Sewer Overflows ("SSOs") and illicit discharges, where the City will spend $50M to $100M over the next ten years to address infrastructure problems related to these issues.
-
2012 - Sterling Suffolk Racecourse LLC Action: As a result of EPA enforcement action under the Clean Water Act, Sterling Suffolk Racecourse LLC (Suffolk Downs) was required to pay a civil penalty of $1.25 million and will perform three environmental projects that provide water quality monitoring and protection. The settlement required the facility to implement green infrastructure and low impact development techniques to address stormwater discharges from the racetrack and maintenance areas of the facility and all construction is now complete.
-
2012 - City of Boston Consent Decree: EPA and the Department of Justice negotiate a Consent Decree with the City of Boston to address Sanitary Sewer Overflows ("SSOs") and illicit discharges and to address infrastructure problems related to these issues
-
2013 - Mystic River Watershed Federal Partnership: EPA's Office of Water announces the Mystic River Watershed’s designation as an Urban Water's Federal Partnership Location. This exciting partnership reconnects urban communities, particularly those that are overburdened or economically distressed, with their waterways by improving coordination among federal agencies and collaborating with community-led efforts to improve our nation’s water systems and promote their economic, environmental, and social benefits.
-
2014 - Final National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits for seven bulk petroleum storage facilities to meet the requirements of the Clean Water Act. On September 24, 2014, EPA Region 1 (EPA) and the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (MassDEP) reissued seven NPDES permits to require wastewater treatment and regulate the pollutant discharges from these seven facilities located along Chelsea River in Chelsea, Revere and East Boston. Along with these draft and final permits EPA conducted several public meeting to enhance community information, participation, and outreach, and issued an Environmental Justice Analysis prepared in support of the permitting actions.
-
2015 - Improved Grading System: EPA and MyRWA develop an improved system to assign water quality grades to the Mystic River and its tributaries. The increased availability of data allows for segments of the watershed to be assigned individual grades based on bacteria levels instead of one grade to describe all segments of the watershed. This new system indicates that water quality in some parts of the watershed is quite good, while other parts still need improvement.
-
2015 - EPA launched a Mystic River water quality monitoring buoy in front of the Blessing of the Bay Boathouse in the City of Somerville. The buoy measures a number of water quality parameters such as temperature, dissolved oxygen, pH, turbidity, specific conductance, and chlorophyll that can be viewed by the public in near real time, and data is made available on EPA's Mystic River Website. In addition to providing real-time water quality data to the public, the buoy is used to monitor for and track cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) blooms.
-
2016 - Phosphorous Loading Studies: EPA and MyRWA with support for USGS and MWRA, begin to examine how high levels of phosphorous, from stormwater runoff, are impacting the watershed. EPA and MyRWA also explore effective ways to reduce phosphorous loading throughout the watershed.
-
2016 - The main stem of the lower Mystic River earns an A- for bacterial water quality (for calendar year 2015).
-
2016 - Final Massachusetts MS4 General Permit. In April 2016 EPA issued a final stormwater general permit updating requirements for small "Municipal Separate Storm Sewer Systems" (MS4) located in Massachusetts. The new permit will enhance stormwater management efforts across Massachusetts, better protecting rivers, streams, ponds, lakes and wetlands from pollutants including elevated levels of nutrients, which are causing algae blooms and other problems in many Massachusetts communities. The permit conditions apply to all communities in the Mystic River Watershed. Special conditions for the reduction of phosphorus and pathogen found in stormwater are included in the permit for all Mystic River Watershed communities.


