BASINS Framework and Features
BASINS enables users to efficiently access nationwide environmental databases and local user-specified datasets, apply assessment and planning tools, and run a variety of proven nonpoint loading and water quality models within a single GIS format. Integration of these resources improves efficiency and reduces the time that it takes to perform environmental investigations on a watershed scale. BASINS can be used by national, state or local governments, environmental organizations, or researchers for environmental management planning and decision making.
Overview
BASINS provides a framework that brings together modeling tools and environmental spatial and tabular data into a geographic information system (GIS) interface. BASINS can be used for investigations and analysis on a variety of geospatial scales from small watersheds within a single municipality, to a large watershed across several states.
 Screen image of BASINS software components list
Screen image of BASINS software components list
BASINS uses a non-proprietary, open-source GIS foundation. This allows BASINS to function independently from any proprietary GIS platforms, while accommodating users of different GIS software platforms. The software architecture of BASINS separates interface components and GIS functions. This enables data from BASINS to be migrated to other GIS platforms and accommodates future updates to supported GIS packages.
BASINS also utilizes “plug-ins”, or a set of software components, that adds several models, utilities, and tools. The plug-ins provide essential functionality for BASINS, and include a “Data Download” feature for downloading spatial and time series data. Other plug-ins provide additional GIS, time series, model setup analysis, and computation utilities.
Users can start new projects by using the “Build BASINS Project” option to extract environmental data for a specific geographic area; an internet connection is required to access the data. Users can also create projects from existing MapWindow projects, or create a project that is a subset of an existing BASINS project. Finally, a user can take an existing BASINS project and open an ArcView or ArcGIS project using the same BASINS data layers, use the more powerful GIS capabilities of ArcView and ArcGIS to manipulate those layers as desired, and then return to BASINS. BASINS project files are stored locally on a computer’s hard drive. The BASINS User’s Manual provides additional information on options for creating projects.
Data
BASINS includes a variety of databases that can be used for watershed-based analysis and modeling. Databases contain information from a wide range of national sources, and are selected on the relevance to environmental analysis, national availability, and scale. The core data included within BASINS are intended to provide some basic water quality modeling inputs, but users can also import their own data sets or higher resolution layers into BASINS. As new data become available, updates will be distributed through the BASINS software.
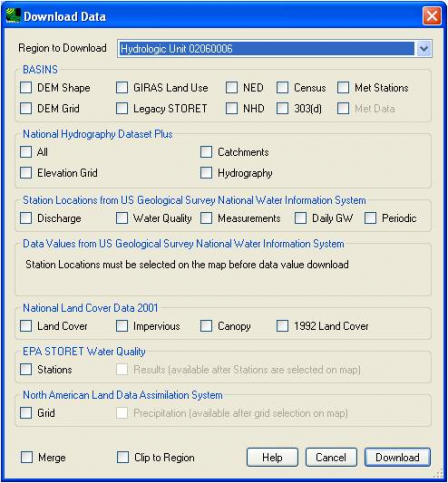 Screen image of BASINS data download toolThe core data included in BASINS fall into four main categories:
Screen image of BASINS data download toolThe core data included in BASINS fall into four main categories:
- Base Cartographic Data
BASINS' base cartographic data include administrative boundaries, hydrologic boundaries, and major road systems. These data are essential for defining and locating study areas and defining watershed drainage areas. - Environmental Background Data
Environmental background data include information on soil characteristics, land use layers, and the stream hydrography. These data provide information to support watershed characterization and environmental analyses. - Monitoring Data
Data from several existing national water quality, meteorological, stream flow and groundwater monitoring databases from US EPA, NOAA, NASA and USGS, were converted into locational data layers. These data layers can facilitate the assessment of water quality conditions and the prioritization and targeting of water bodies and watersheds. - Point Source Data
Point source discharge data, including location, type of facility, and estimated loading are provided. These data are used to support evaluation of watershed-based loading summaries combining point and nonpoint sources.
BASINS creates a dynamic link to data generated in the GIS environment that allows information to be passed directly to the models. The data resulting from simulation models can be displayed visually and can be used to perform further analysis and interpretation.
This page provides links to non-EPA web sites that provide additional information about this topic. You will leave the EPA.gov domain, and EPA cannot attest to the accuracy of information on that non-EPA page. Providing links to a non-EPA Web site is not an endorsement of the other site or the information it contains by EPA or any of its employees. Also, be aware that the privacy protection provided on the EPA.gov domain (see Privacy and Security Notice) may not be available at the external link. The following links exit the site Exit
Within the “Download Data” plug-in, users can access the following datasets:
- BASINS Pre-preprocessed Datasets
Datasets under the “BASINS” category have been pre-processed for BASINS and are stored on an EPA server for download. The following data are pre-processed for use in BASINS:- Digital Elevation Model (DEM): Shape
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM): Grid
- Geographic Information Retrieval and Analysis System (GIRAS): Land Use
- Legacy STORET
- National Elevation Dataset (NED) National Map: Elevation
- National Hydrography Dataset (NHD)
- U.S. Census
- 303(d) Impaired Waters
- Meteorological (Met) Data
- NHD Plus
Within the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) Plus group are options to download the elevation grid, catchments shapefiles, hydrography shapefiles, plus an option to download all NHDPlus layers. - USGS Stations from NWIS
The 'Station Locations from US Geological Survey National Water Information System' options download station locations for the selected station types. Station locations are available for 'Daily Discharge', 'Water Quality', 'Measurements' and 'Ground Water'. - USGS Data from NWIS
The 'Data Values from US Geological Survey National Water Information System' options download data values collected at the selected USGS station locations. Station locations must first be downloaded and then individual stations must be selected on the map before downloading data values. After downloading, data values are stored in the NWIS folder within the BASINS project. - National Land Cover Data (NLCD) 2001
The 'National Land Cover Data' group is used to download GIS layers from the NLCD dataset. Layers from the 2001 dataset available for download include the land cover, impervious, and canopy grids. The 1992 Land Cover grid from NLCD is also available for download to allow users to examine differences in historic and current land cover. Once downloaded, the grids will be projected and loaded onto the BASINS map. - EPA STORET Water Quality Data
The 'Modernized STORET' option downloads data from the EPA STORET data site. Options are available to download STORET stations as well as the results, or data values. - North American Land Data Assimilation System (NLDAS)
Precipitation data from NLDAS (North American Land Data Assimilation System) Phase 2 can be added to the BASINS project. - Metadata
Metadata or "data about data" describes the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics of data. EPA’s BASINS Metadata webpage contains metadata for the various data used by BASINS.
Tools and Utilities
BASINS includes tools and utilities for assessing watershed conditions to help users understand water quality issues and pollution sources in a watershed, assess monitoring programs, identify data gaps, and develop watershed-water quality modeling strategies.
Further, BASINS includes tools designed to assist in summarizing key watershed information in a format suitable for preparing Watershed Characterization Reports (tables that inventory and characterize both point and nonpoint sources at the watershed and subwatershed scales).
Environmental Assessment Tools:
- Watershed Characterization Reports
BASINS 4 provides users the capability to generate eight different types of watershed characterization reports in tabular format.- 1990 Population and Sewerage by Census Tract
- 2000 Population and Census Tract Table
- 303d Listed Segment Tables
- Landuse Distribution Table
- Permitted Point Source Facilities Table
- Point Source Discharge Concentration and Loading Table
- Water Quality Observations Stations Table
- Watershed Characterization System
The BASINS Watershed Characterization System creates customizable reports to describe the physical characteristics of watersheds (sub-basins) users have defined. The following reports are available:- Water Bodies & 303d
- Population Estimates
- Housing and Sewage
- Soil Characteristics
- Land use Characterization
- Permitted Point Sources
- Data Summary
Utilities:
- GenScn
BASINS includes the program GenScn, originally developed by the U.S. Geological Survey, which facilitates the display and interpretation of output data derived from model applications. This tool allows users to select display locations and time periods. Displays are in graphical and tabular form. GenScn displays a variety of data formats, including HSPF simulation output, BASINS water quality observation data, and USGS flow data, and SWAT output data. It also performs statistical functions and data comparisons. Due to its ability to display and compare observed and modeled data, the postprocessor is a useful tool in model calibration and environmental systems analysis. Note: Beginning with BASINS 4.1, GenScn is available as a separate download at http://www.aquaterra.com/basins4. Most of the functionality of GenScn is now included in the core BASINS user interface. - WDMUtil
WDMUtil is a utility program for managing Watershed Data Management (WDM) files, which contains input and output time-series data for HSPF. Note: Beginning with BASINS 4.1, WDMUtil is available as a separate download at http://www.aquaterra.com/basins4. Most of the functionality of WDMUtil is now included in the core BASINS user interface. - Manual Watershed Delineation Tool
The BASINS Manual Watershed Delineation tool allows the user to delineate subwatersheds manually. It allows the user to subdivide a watershed into several smaller hydrologically connected watersheds based on the user's knowledge of that watershed's drainage topography. The tool also provides users the flexibility to edit shapes and attributes of manually delineated watersheds, outlets and generating stream networks. - Automatic Watershed Delineation Tool
The BASINS Automatic Watershed Delineation tool allows the user to delineate subwatersheds based on an automatic procedure using Digital Elevation Model (DEM) data. User specified parameters provide limits that influence the size and number of subwatersheds created. - Land Use Reclassification
The Land Use Reclassification tool assists the user in grouping or renaming land use categories as needed to support modeling and analysis. Land uses can be reclassified in one of two ways: reclassification of the entire layer (all land uses) or reclassification of selected layers (single or multiple land uses from within an entire layer). - Lookup Tables
The Lookup Tables provide users quick access to relevant reference information on data products included within BASINS. Information is provided for products such as the map projection, definition of agency codes for monitoring data, Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes, and the water quality criteria and threshold values of selected pollutants.
Models
BASINS provides plug-ins to set up watershed and water quality simulation models based on information in the BASINS project. By using plug-ins, BASINS aids the user in setting up powerful external, yet linked, simulation models. Additional information on each model can be found in the BASINS User’s Manual.
The following models are available in BASINS 4.1:
Watershed Models:
- Hydrological Simulation Program - FORTRAN (HSPF)
HSPF is a watershed model that simulates nonpoint source runoff and pollutant loadings for a watershed, combines these with point source contributions, and performs flow and water quality routing in reaches. WinHSPF is designed to interact with the BASINS utilities and data sets to facilitate the extraction of appropriate information and the preparation of model input files. - The Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT)
SWAT is a physically based continuous simulation model useful for predicting the impact of land management practices on water, sediment, and different agricultural chemical yields from watersheds of various scales and complexities. - The EPA Storm Water Management Model (SWMM)
SWMM is a dynamic rainfall-runoff simulation model used for single event or long-term (continuous) simulation of runoff quantity and quality from primarily urban areas. SWMM is widely used for planning, analysis and design related to storm water runoff, combined sewers, sanitary sewers, and other drainage systems in urban areas, with many applications in non-urban areas as well. - Generalized Watershed Loading Function model extension (GWLF-E) MapShed
The GWLF-E Plug-in included with BASINS is a GIS-based watershed modeling tool that estimates monthly nutrient and sediment loads within a watershed. This plug-in provides a link between BASINS and the newest version of the GWLF watershed model (now called GWLF-E). - The Pollutant Loading Estimator (PLOAD)
PLOAD is a simple watershed model that computes nonpoint source loads from different subwatersheds and landuses based on annual precipitation, land uses and BMPs. PLOAD estimates nonpoint sources of pollution on an annual average basis, for any user-specified pollutant, using either the export coefficient or simple method approach.
Instream / Water Quality Models:
- AQUATOX
AQUATOX is a time-variable ecological risk assessment model that simulates the fate and effects of various environmental stressors in aquatic ecosystems. It simulates the fate and transfer of pollutants from loads to the water, sediments, and biotic components, and transfer throughout the food web. AQUATOX version 3 is supported in BASINS. - Water Quality Analysis Simulation Program (WASP)
WASP is a dynamic compartment-modeling program for aquatic systems, including both the water column and the underlying benthos. BASINS allows the user to build a new project and open WASP directly from the BASINS user interface.
The following table provides information on the method of distribution, and the documentation locations, for the models contained, or compatible with, BASINS. BASINS provides plug-ins to expedite the setup of each of these models from spatial and time series data. Each model's setup plug-in is distributed with the core BASINS installation package.
| Model | Core Model Distribution | Core Model Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| HSPF | Installed as part of BASINS | hspf.chm in BASINS 'Docs' folder |
| SWAT | http://swat.tamu.edu/ | Installed with core model |
| AQUATOX | http://www2.epa.gov/exposure-assessment-models/aquatox | Installed with core model |
| WASP | http://www2.epa.gov/exposure-assessment-models/water-quality-analysis-simulation-program-wasp | Installed with core model |
| SWMM | http://www2.epa.gov/water-research/storm-water-management-model-swmm | Installed with core model |
| GWLF-E | Installed as part of BASINS | GWLFManual.pdf in BASINS 'Docs' folder |
| PLOAD | Installed as part of BASINS | Documented within the BASINS Users Manual |
Analysis Tools and Postprocessors
- GenScn Postprocessor
BASINS includes the program GenScn, originally developed by the U.S. Geological Survey, which facilitates the display and interpretation of output data derived from model applications. This tool allows users to select display locations and time periods. Displays are in graphical and tabular form. GenScn displays a variety of data formats, including HSPF simulation output, BASINS water quality observation data, and USGS flow data, and SWAT output data. It also performs statistical functions and data comparisons. Due to its ability to display and compare observed and modeled data, the postprocessor is a useful tool in model calibration and environmental systems analysis. Note: Beginning with BASINS 4.1, GenScn is available as a separate download at http://www.aquaterra.com/basins4. Most of the functionality of GenScn is now included in the core BASINS user interface. - Climate Assessment Tool (CAT)
The BASINS Climate Assessment Tool (CAT) provides a flexible set of capabilities for exploring the potential effects of climate change on streamflow and water quality using different watershed models in BASINS. Tools have been integrated into the BASINS system allowing users to create climate change scenarios by applying change factors to modify historical daily/hourly weather data. These data are then available as meteorological input to different watershed models in BASINS (HSPF, SWAT, and SWMM). A capability is also provided to calculate specific hydrologic and water quality endpoints important to watershed management based on model output (e.g., annual averages, the 100-year flood or 7Q10 low flow event). BASINS CAT can be used to determine the outcomes of a single climate change scenario, or to automate multiple model runs to assess watershed sensitivity to a user-defined range of potential future changes. - DFLOW
DFLOW is a tool to estimate user selected design stream flows for low flow analysis and water quality standards. DFLOW is useful to regulators in state and EPA regional offices, modelers, or anyone interested in calculating design flow statistics. - Time Series Functions
BASINS contains utilities to manage and analyze available project time-series data. Project time-series data are managed through the Time-Series Management Utilities. The Graph menu item is used to produce graphs of the selected time series. Among the implemented graph types include Timeseries, Flow/Duration, Running Sum, Residual, Cumulative Difference, and Scatter. - USGS Surface Water Statistics
USGS Surface Water Statistics (SWSTAT) contains a set of procedures for statistical analysis of time-series data. SWSTAT contains the following statistical capabilities to support water-quantity and water-quality modeling:- Compute basic statistics for a time series.
- Perform flow-duration analysis using values from a time-series data set.
- Compute absolute errors, standard errors, and an error matrix for two time-series data sets.
- Compute an n-day high or low annual time series from a daily time series.
- Perform frequency analysis of any annual time series using the log-Pearson Type III distribution.
- Perform Kendall Tau analysis for trend in annual time series.
- Compute duration hydrograph tables and curves.
