Climate Change Indicators: U.S. and Global Precipitation
This indicator describes trends in average precipitation for the United States and the world.
-
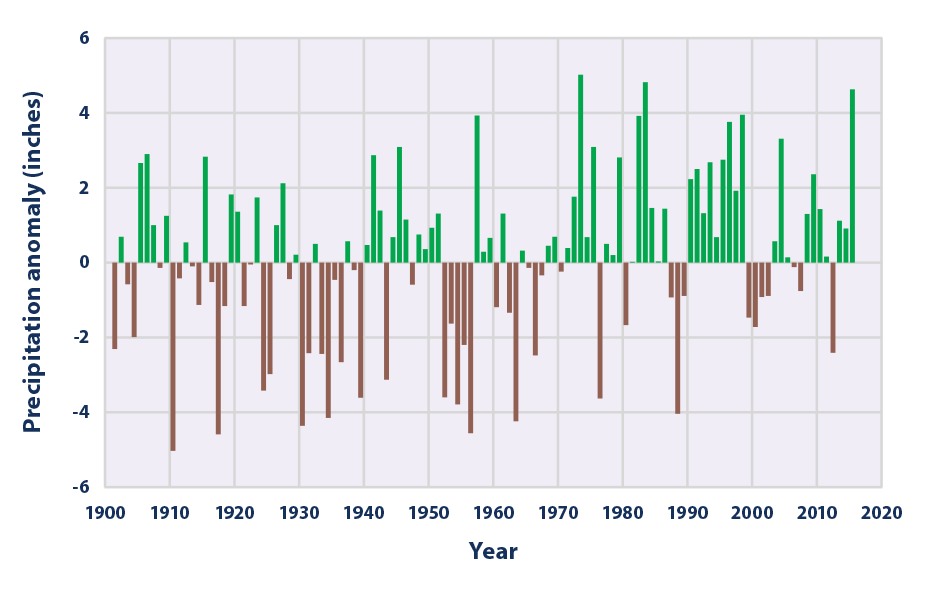
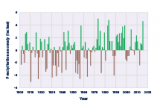
This figure shows how the total annual amount of precipitation in the contiguous 48 states has changed since 1901. This graph uses the 1901–2000 average as a baseline for depicting change. Choosing a different baseline period would not change the shape of the data over time.
Data source: NOAA, 20161
Web update: August 2016 -
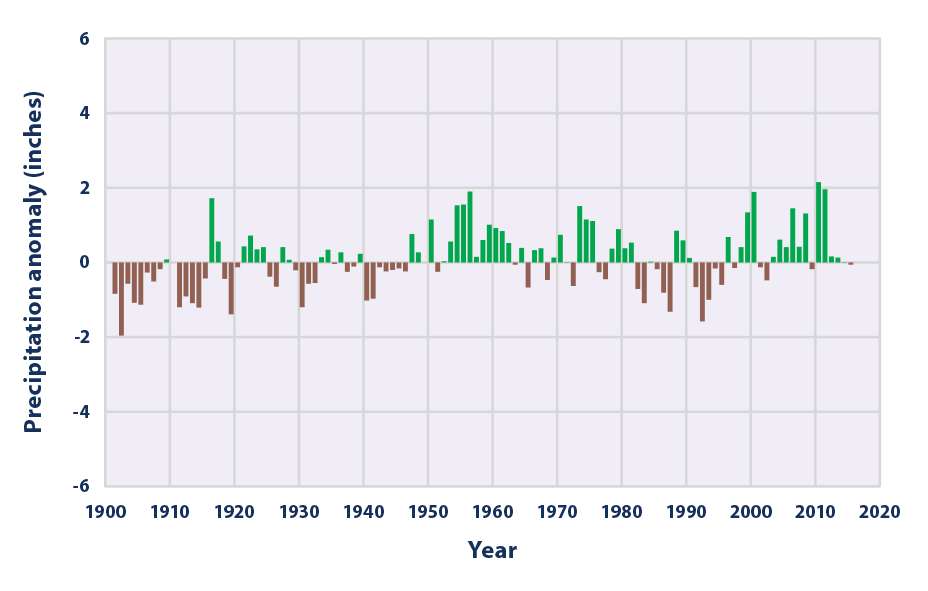
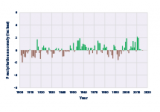
This figure shows how the total annual amount of precipitation over land worldwide has changed since 1901. This graph uses the 1901–2000 average as a baseline for depicting change. Choosing a different baseline period would not change the shape of the data over time.
Data source: Blunden and Arndt, 20162
Web update: August 2016 -
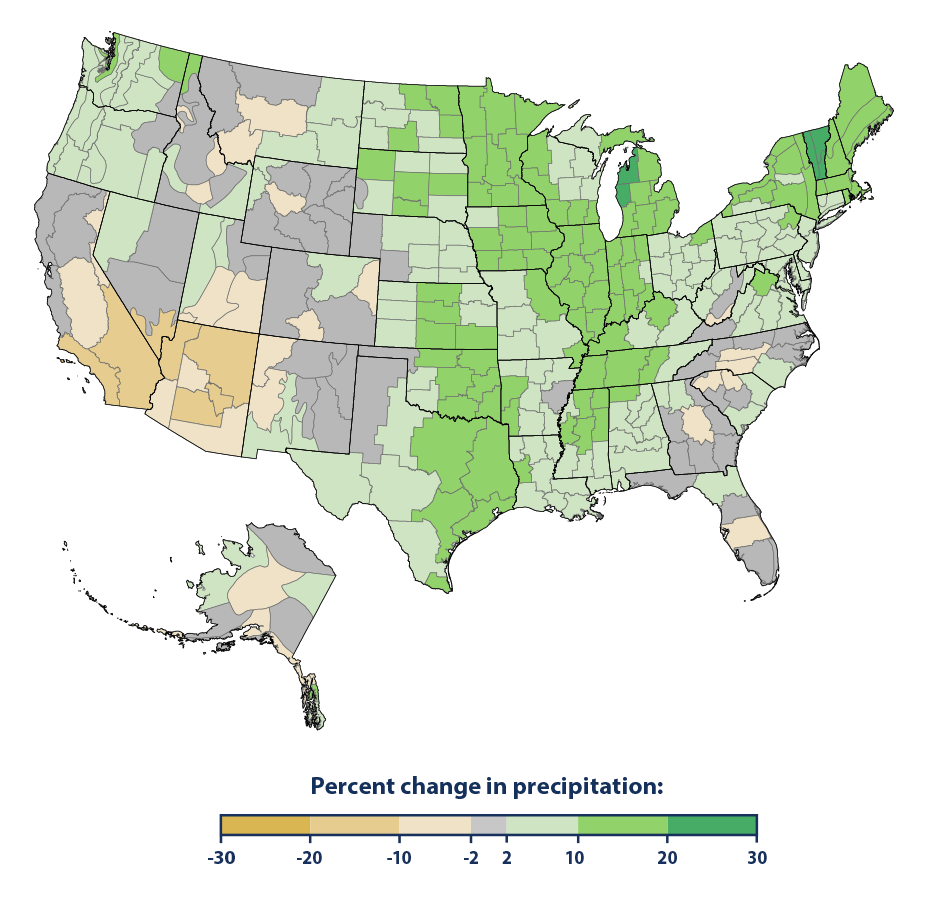
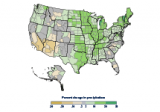
This figure shows the rate of change in total annual precipitation in different parts of the United States since the early 20th century (since 1901 for the contiguous 48 states and 1925 for Alaska). The data are shown for climate divisions, as defined by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Data source: NOAA, 20163
Web update: August 2016
Key Points
- On average, total annual precipitation has increased over land areas in the United States and worldwide (see Figures 1 and 2). Since 1901, global precipitation has increased at an average rate of 0.08 inches per decade, while precipitation in the contiguous 48 states has increased at a rate of 0.17 inches per decade.
- Some parts of the United States have experienced greater increases in precipitation than others. A few areas, such as the Southwest, have seen a decrease in precipitation (see Figure 3). Not all of these regional trends are statistically significant, however.
Background
Precipitation can have wide-ranging effects on human well-being and ecosystems. Rainfall, snowfall, and the timing of snowmelt can all affect the amount of surface water and groundwater available for drinking, irrigation, and industry. They also influence river flooding and can determine what types of animals and plants (including crops) can survive in a particular place. Changes in precipitation can disrupt a wide range of natural processes, particularly if these changes occur more quickly than plant and animal species can adapt.
As average temperatures at the Earth’s surface rise (see the U.S. and Global Temperature indicator), more evaporation occurs, which, in turn, increases overall precipitation. Therefore, a warming climate is expected to increase precipitation in many areas. Just as precipitation patterns vary across the world, however, so do the precipitation effects of climate change. By shifting the wind patterns and ocean currents that drive the world’s climate system, climate change will also cause some areas to experience decreased precipitation. In addition, higher temperatures lead to more evaporation, so increased precipitation will not necessarily increase the amount of water available for drinking, irrigation, and industry (see the Drought indicator).
About the Indicator
This indicator examines U.S. and global precipitation patterns, based on rainfall and snowfall measurements from land-based weather stations worldwide. This indicator starts at 1901 except for the detailed map of Alaska, where reliable statewide records are available back to 1925. The indicator extends through 2015.
This indicator shows annual anomalies, or differences, compared with the average precipitation from 1901 to 2000. At each weather station, annual precipitation anomalies were calculated from total annual precipitation in inches. Anomalies for the contiguous 48 states and Alaska have been determined by calculating average precipitation anomalies for areas within each state based on station density and topography. These regional anomalies are then averaged together in proportion to their area to develop national results. Similarly, global anomalies have been determined by dividing the world into a grid, averaging the data for each cell of the grid, and then averaging the grid cells together.
Indicator Notes
Data from the early 20th century are somewhat less precise because there were fewer stations collecting measurements at the time. To ensure that overall trends are reliable, the data have been adjusted where possible to account for any biases that might be introduced by factors such as station relocation or changes in measurement instruments.
Hawaii and U.S. territories are not included, due to limitations in available data.
Data Sources
The data for this indicator were provided by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s National Centers for Environmental Information, which maintains a large collection of climate data online at: www.ncei.noaa.gov. The precipitation anomalies shown here were calculated based on monthly values from a network of long-term monitoring stations.
Technical Documentation
References
1 NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). 2016. National Centers for Environmental Information. Accessed February 2016. www.ncei.noaa.gov.
2 Blunden, J., and D.S. Arndt (eds.). 2016. State of the climate in 2015. B. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 97(8):S1–S275.
3 NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). 2016. National Centers for Environmental Information. Accessed February 2016. www.ncei.noaa.gov.